filmov
tv
Calculating E from V(x,y,z): E = - potential gradient | Electrostatic potential | Khan Academy
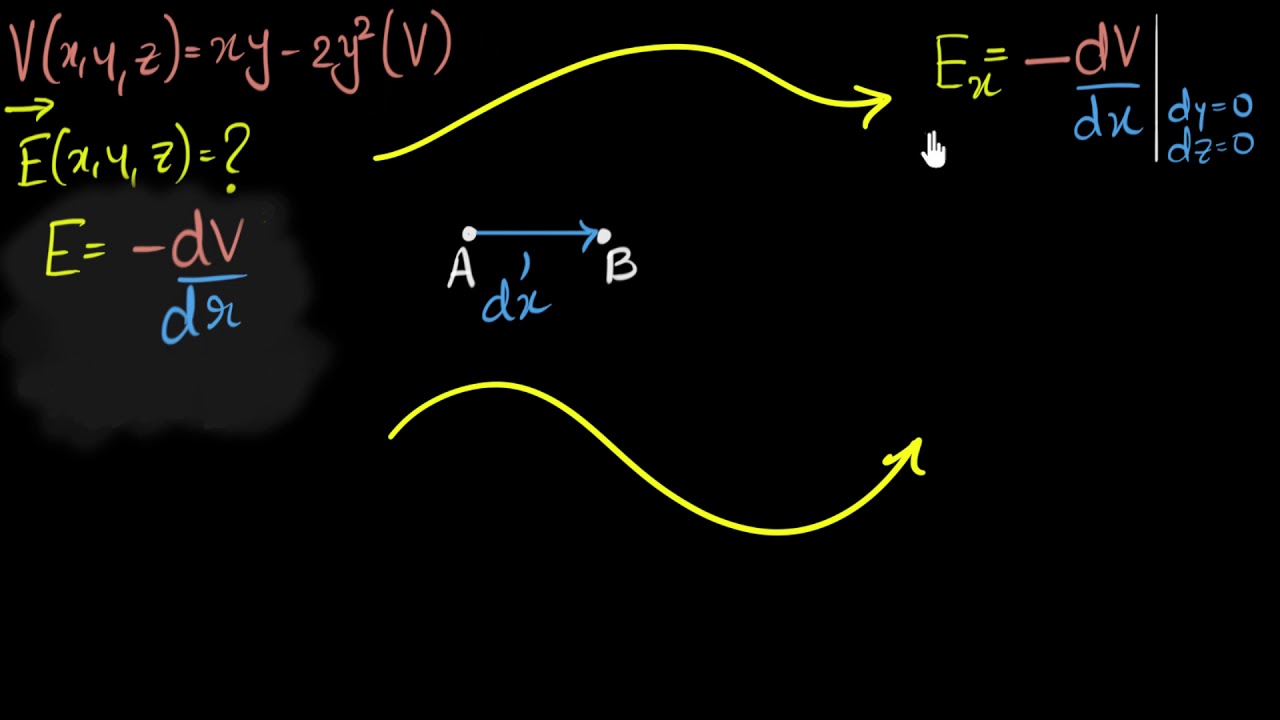
Показать описание
Let's calculate the electric field vector by calculating the negative potential gradient. We first calculate individually calculate the x,y,z component of the field by partially differentiating the potential function.
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help!
Created by Mahesh Shenoy
Calculating E from V(x,y,z): E = - potential gradient | Electrostatic potential | Khan Academy
Partial Derivatives of z =e^(xy)
How to Find Partial Derivatives (e^-xyz Example) | Multivariable Calculus Tutorial
e^(iπ) in 3.14 minutes, using dynamics | DE5
If z=f(x y) x=e^u+e^-v y=e^-u-v show Әz/Әu - Әz/Әv = xӘu/Әx - yӘu/Әy PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION...
The electric potential V at any point (x,y,z) is given by V=3x^2 where x is in meters and V in . . .
Approximate the Change in z using the Total Differential for z = e^(x + y)
The electric potential at a point (x, y, z) is given by V= -x 2 y-x z 3+4. The electric field at
5. Zero Initial Velocity problems for 1D wave Equation
The electric potential at a point ( x y z ) is given by V = - x^2 y - xz ^3 +4 The electric field ve
The electric potential V at any point (x, y, z), all in meters in space is given by V=4 x 2 volt.
Partial Differentiation Example of total Differentiation If z=f(x, y) and x=e^u cos(v), y=e^u sin(v)
The electric potential V at any point (.x, y, z), all in metres in space is given by V = 4x2 volt.
The electric potential `V` at any point `(x,y,z)`, all in meters in space is given by `V= 4x^(2)`
Find the Total Differential of the Multivariate Function f(x,y,z) = e^(x^2 + y^2 + z^2)
In a region, the potential is respresented by `V(x, y, z) = 6x - 8xy - 8y + 6yz`, where `V` is i
Solve: Z= e^my Φ(x-y) | Formation of PDE by eliminating arbitrary functions.
how to plot a point on xyz
Calibrate Your XY & Z Steps For Dimensional Accuracy of Your 3D Prints
The electric potential existing in space is V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx). (a) Write the dimensional
Find the Equation of the Tangent Plane to the Surface z = 4x^2 - y^2 + 2y at (-1, 2, 4)
[Complex Analysis] How to Solve the Equation e^z = -2
Express the integral f(x, y, z) dV E six different ways, where E is bounded by y = x^2, z=0, y+2z=4
What is a vector? - David Huynh
Комментарии
 0:13:39
0:13:39
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:03:47
0:03:47
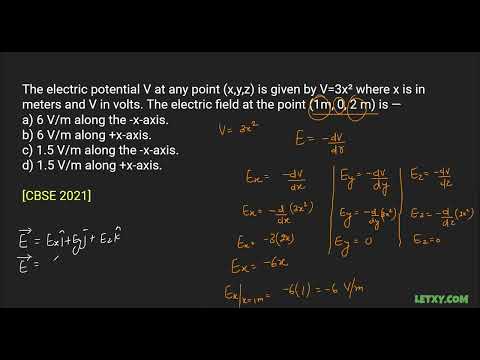 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:11:35
0:11:35
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:03:47
0:03:47
![[Complex Analysis] How](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pybSBnnbKjg/hqdefault.jpg) 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:19:08
0:19:08
 0:04:41
0:04:41