filmov
tv
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (1 out of 2)
Показать описание
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) allows the determination of crystallographic density and hence crystal structure of unknown crystalline solids. X-rays are diffracted by atoms in a plane and a spherical wave is radiated. If there are two or more such scattering centres, the spherical waves at specific angles reinforce one another (constructive interference) and at other angles cancel one another (destructive interference). A crystal with planes oriented at an angle θ to an incident x-ray beam of wavelength λ will diffract the rays according to Bragg's equation: 2dsinθ = nλ.
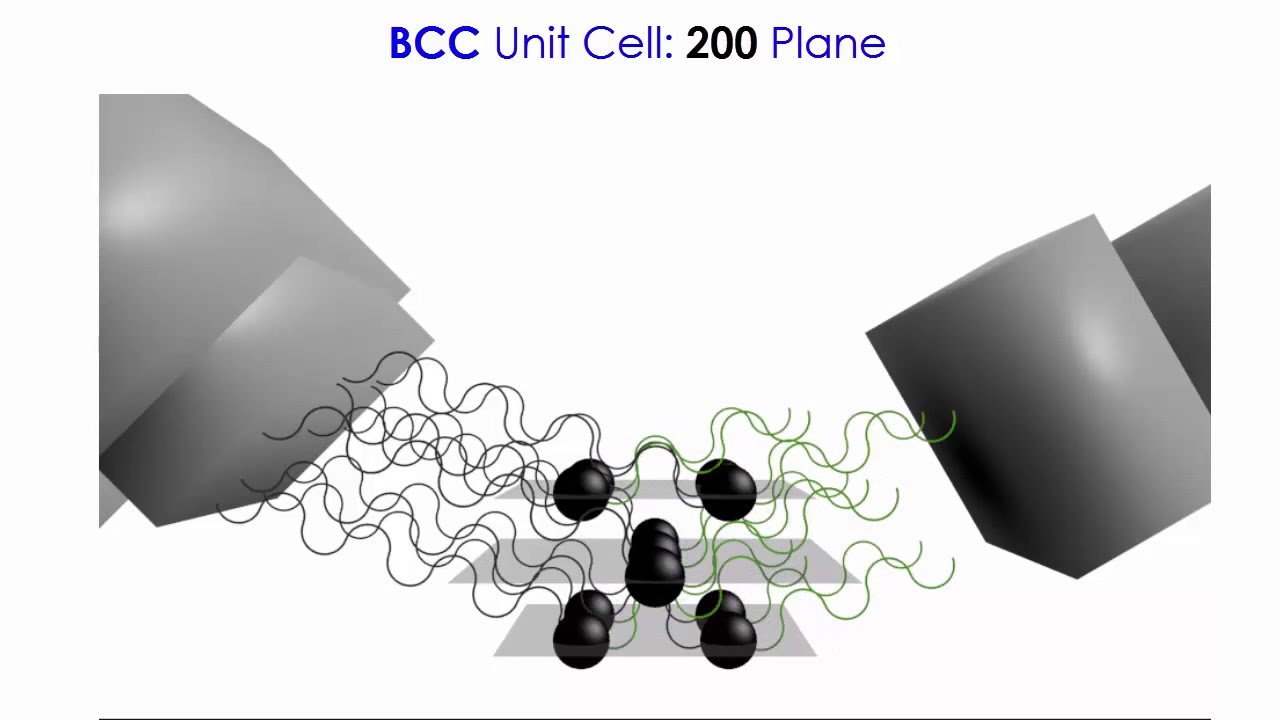
In video (1 out of 2), the concept of XRD will be illustrated for compound Tungsten which has a BCC structure using planes 110 and 200.
In video (2 out of 2), with the Bragg’s angle θ obtained from the Powder XRD Spectrum, the unit cell length and volume and hence the experimental crystallographic density (g/cm3) is calculated. Interplanar distance is also determined.
In video (1 out of 2), the concept of XRD will be illustrated for compound Tungsten which has a BCC structure using planes 110 and 200.
In video (2 out of 2), with the Bragg’s angle θ obtained from the Powder XRD Spectrum, the unit cell length and volume and hence the experimental crystallographic density (g/cm3) is calculated. Interplanar distance is also determined.
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (1 out of 2)
Powder X Ray Diffraction familiarisation video
What is X-ray Diffraction?
Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD) for Pharmaceuticals
What is Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction?
X-ray diffraction analysis: 2theta-theta and GIXRD scan
Powder X- Ray Diffraction (P-XRD) Technique
XRD Sample Preparation - Back Loaded Sample Holder - X-ray Diffraction
Introduction to (powder) x-ray Diffraction
Powder X-Ray Diffraction (2 out of 2)
1 Crystal Structure 1.28 X-Ray Diffraction Methods :Powder Method #XRayDiffraction #PowderMethod
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD)
Tutorial videos to improve your powder X-ray diffraction analysis
Single Crystal X Ray Diffraction familiarisation video
Single Crystal XRD Vs Powder XRD
Practical introduction to X-ray diffraction - Powder diffraction - video 2 of 4
Rietveld Refinement of X-ray Diffraction Data Using FullProf Package - Part I
X-Ray diffraction (XRD) #characteization#techniques #pysiomania#science
21. X-ray Diffraction Techniques I (Intro to Solid-State Chemistry)
X ray Diffraction – Solving Problems with Phase Analysis
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Basic Operation
Powder X-Ray Diffractometer -Lab
Diffraction Lecture 17: Indexing Diffraction Patterns of Cubic Crystals
X-Ray DIFFRACTION LAB at NISER 🔥
Комментарии
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:28:50
0:28:50
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:21:02
0:21:02
 0:47:16
0:47:16
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:29:41
0:29:41
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:50:16
0:50:16
 0:27:45
0:27:45
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:30:54
0:30:54
 0:26:11
0:26:11
 0:00:42
0:00:42