filmov
tv
Capacitors & Inductors in Series and Parallel | Circuit Analysis Made Easy

Показать описание
Unlock the secrets of **Capacitors** and **Inductors** in **Series and Parallel** configurations with this clear and concise tutorial from the **Basic Electrical Engineering** playlist. Learn how these key circuit elements behave when combined in different configurations, and how to calculate their **equivalent capacitance** and **equivalent inductance**. Perfect for **engineering students**, **high school physics learners**, and those preparing for **AP/IB Physics**. Master the essential concepts of **circuit analysis** to excel in your studies and exams!
🔑 **Key Topics**:
- Series vs Parallel configurations of Capacitors and Inductors
- How to calculate total capacitance and inductance
- Real-world applications in AC/DC circuits
- Impact on steady-state and transient response
Hashtags: **#Capacitors #Inductors #SeriesParallel #CircuitAnalysis #ElectricalEngineering #EngineeringEssentials #BasicElectricalEngineering #APPhysics #IBPhysics**
### Technical Descriptions:
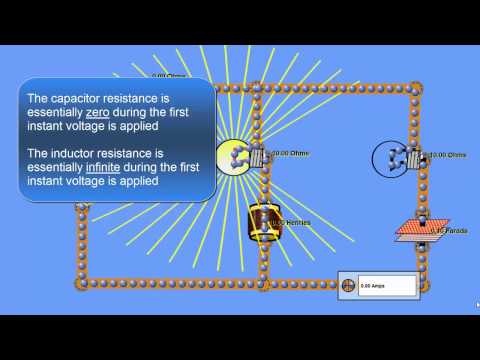
- **Capacitors in Series**: The total or equivalent capacitance is less than the smallest individual capacitance, calculated using the reciprocal sum formula.
- **Capacitors in Parallel**: The total capacitance is the sum of all individual capacitances, resulting in a larger overall capacitance.
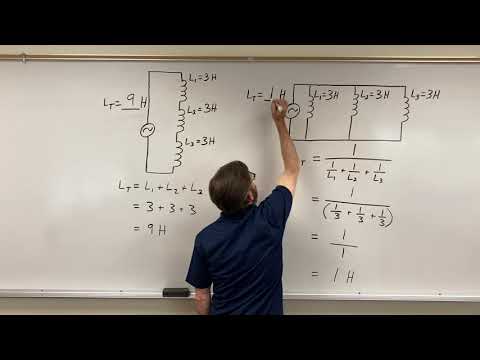
- **Inductors in Series**: The equivalent inductance is the sum of all individual inductances, leading to a larger total inductance.
- **Inductors in Parallel**: The total or equivalent inductance is less than the smallest individual inductance, calculated similarly to capacitors in series, using the reciprocal sum formula.
"Explore the behavior of capacitors and inductors in series and parallel combinations with this in-depth analysis! Learn how to tackle these basic circuit elements with powerful techniques like Mesh Analysis, Node Analysis, Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL), and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). Ideal for first-year engineering students, Class 11/12 learners, and those preparing for competitive exams like IIT JEE and NEET. Boost your understanding of electrical circuits for AP and IB Physics courses too. #Capacitors #Inductors #SeriesParallelCircuits #MeshAnalysis #NodeAnalysis #KCL #KVL #ElectricalEngineering #IITJEE #NEET #APPhysics #IBPhysics #FirstYearEngineering #Class12Physics"
Capacitors & Inductors in Series/ Parallel Combination #electronicsengineering #eranand
Inductors in Series
Inductors in Parallel
Capacitors in Series
Capacitors in Parallel
## Elementary Circuit Elements
An electric circuit is a closed loop or path that allows electric current to flow. Circuits are made up of electrical components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, that are connected by wires. The components in a circuit can be used to perform a variety of functions, such as amplifying signals, filtering noise, and storing energy.
The most basic type of circuit is a series circuit. In a series circuit, the components are connected in a single loop. The current that flows through each component in a series circuit is the same. The voltage across each component in a series circuit adds up to the total voltage of the circuit.
The next most basic type of circuit is a parallel circuit. In a parallel circuit, the components are connected in multiple loops. The current that flows through each component in a parallel circuit is determined by the resistance of that component. The voltage across each component in a parallel circuit is the same as the voltage of the source.
In addition to series and parallel circuits, there are many other types of circuits, such as bridge circuits, feedback circuits, and oscillator circuits. Each type of circuit has its own unique properties and applications.
## Circuit Components
The basic components of an electric circuit are:
Sources:
Sources provide the energy that powers the circuit. Common sources include batteries, generators, and solar cells.
Loads:
Loads are devices that consume power from the circuit. Common loads include light bulbs, motors, and computers.
Resistors:
Resistors resist the flow of current. They are used to control the current in a circuit and to drop voltage.
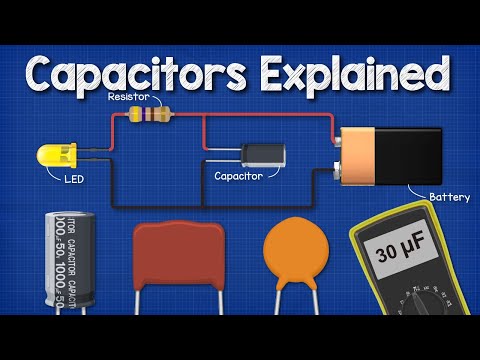
Capacitors:
Capacitors store electrical energy. They are used to filter noise, smooth out voltage, and store energy for later use.
Inductors:
Inductors store energy in the form of a magnetic field. They are used to filter noise, boost voltage, and store energy for later use.
🔑 **Key Topics**:
- Series vs Parallel configurations of Capacitors and Inductors
- How to calculate total capacitance and inductance
- Real-world applications in AC/DC circuits
- Impact on steady-state and transient response
Hashtags: **#Capacitors #Inductors #SeriesParallel #CircuitAnalysis #ElectricalEngineering #EngineeringEssentials #BasicElectricalEngineering #APPhysics #IBPhysics**
### Technical Descriptions:
- **Capacitors in Series**: The total or equivalent capacitance is less than the smallest individual capacitance, calculated using the reciprocal sum formula.
- **Capacitors in Parallel**: The total capacitance is the sum of all individual capacitances, resulting in a larger overall capacitance.
- **Inductors in Series**: The equivalent inductance is the sum of all individual inductances, leading to a larger total inductance.
- **Inductors in Parallel**: The total or equivalent inductance is less than the smallest individual inductance, calculated similarly to capacitors in series, using the reciprocal sum formula.
"Explore the behavior of capacitors and inductors in series and parallel combinations with this in-depth analysis! Learn how to tackle these basic circuit elements with powerful techniques like Mesh Analysis, Node Analysis, Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL), and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). Ideal for first-year engineering students, Class 11/12 learners, and those preparing for competitive exams like IIT JEE and NEET. Boost your understanding of electrical circuits for AP and IB Physics courses too. #Capacitors #Inductors #SeriesParallelCircuits #MeshAnalysis #NodeAnalysis #KCL #KVL #ElectricalEngineering #IITJEE #NEET #APPhysics #IBPhysics #FirstYearEngineering #Class12Physics"
Capacitors & Inductors in Series/ Parallel Combination #electronicsengineering #eranand
Inductors in Series
Inductors in Parallel
Capacitors in Series
Capacitors in Parallel
## Elementary Circuit Elements
An electric circuit is a closed loop or path that allows electric current to flow. Circuits are made up of electrical components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, that are connected by wires. The components in a circuit can be used to perform a variety of functions, such as amplifying signals, filtering noise, and storing energy.
The most basic type of circuit is a series circuit. In a series circuit, the components are connected in a single loop. The current that flows through each component in a series circuit is the same. The voltage across each component in a series circuit adds up to the total voltage of the circuit.
The next most basic type of circuit is a parallel circuit. In a parallel circuit, the components are connected in multiple loops. The current that flows through each component in a parallel circuit is determined by the resistance of that component. The voltage across each component in a parallel circuit is the same as the voltage of the source.
In addition to series and parallel circuits, there are many other types of circuits, such as bridge circuits, feedback circuits, and oscillator circuits. Each type of circuit has its own unique properties and applications.
## Circuit Components
The basic components of an electric circuit are:
Sources:
Sources provide the energy that powers the circuit. Common sources include batteries, generators, and solar cells.
Loads:
Loads are devices that consume power from the circuit. Common loads include light bulbs, motors, and computers.
Resistors:
Resistors resist the flow of current. They are used to control the current in a circuit and to drop voltage.
Capacitors:
Capacitors store electrical energy. They are used to filter noise, smooth out voltage, and store energy for later use.
Inductors:
Inductors store energy in the form of a magnetic field. They are used to filter noise, boost voltage, and store energy for later use.
 0:31:34
0:31:34
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:28:18
0:28:18
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 1:45:21
1:45:21
 0:10:57
0:10:57
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:26:56
0:26:56
 0:42:36
0:42:36
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:09:34
0:09:34
 0:16:16
0:16:16
 0:33:43
0:33:43
 0:22:26
0:22:26
 0:05:38
0:05:38