filmov
tv
Special Case : Particular Integral (Exp) : 2nd Order Linear Differential Equation : ExamSolutions

Показать описание
Tutorial on special case and the particular integral.
SUBSCRIBE TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
FOLLOW ME
EXAM SOLUTIONS Is my free website for maths tutorials and maths revision.
SUBSCRIBE TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL
FOLLOW ME
EXAM SOLUTIONS Is my free website for maths tutorials and maths revision.
Special Case : Particular Integral (Exp) : 2nd Order Linear Differential Equation : ExamSolutions
Special Case : Particular Integral (k) : 2nd Order Linear Differential Equation : ExamSolutions
A-Level Further Maths I5-09 2nd Order Differential Equations: Special Cases
Particular integral of special case with solved examples
Particular Integral || Method-6 || Special Case || Linear Differential Equation of Higher Order
Particular Integral ||Special Case || Method-7|| Linear Differential Equation of Higher Order
Problem case to consider for the particular integral
Particular Integral Case 3 || X= x^m || Linear Differential Equation of Higher order
PG TRB particular integral for special case
Particular Integral Case 6 || Case 6_Example 1
Particular Integral Shortcut Method Case-5 | M3
6. Rules for finding Particular Integral | Case#1 | Differential Equations of Higher Order
Differential Equations 3: Particular Integral and Complementary Function Method
Particular Integral Case 6 || Case 6_Example 3 ||
Particular integral of L.D.E. Type 1🔥special case🔥 #particularintegral #shorts #firstyearengineering...
A-Level Further Maths I5-10 2nd Order Differential Equations: Particular Integrals Overview
Rules for finding particular integral | special case | differential equations | finding cf and pi #1
Linear Differential Equations | Particular Integral | Shortcut Method | Rounak Sir
Undetermined Coefficients: Solving non-homogeneous ODEs
Particular Integral Shortcut Method Case-4 | M3
Method of Undetermined Coefficients - Nonhomogeneous 2nd Order Differential Equations
Particular Integral case 1 || Linear Differential Equation of Higher order
PARTICULAR INTEGRAL -I @VATAMBEDUSRAVANKUMAR
Particular integral (special case)
Комментарии
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:28:18
0:28:18
 0:29:14
0:29:14
 0:32:27
0:32:27
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:12:18
0:12:18
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:13:36
0:13:36
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:06:29
0:06:29
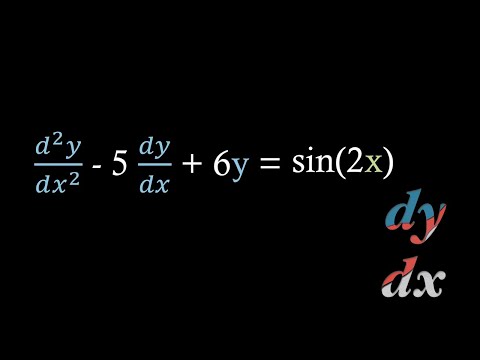 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:53:13
0:53:13
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:41:28
0:41:28
 0:19:01
0:19:01
 0:31:08
0:31:08
 0:10:18
0:10:18