filmov
tv
autoimmune thyroiditis

Показать описание
(Hashimoto's disease, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis)
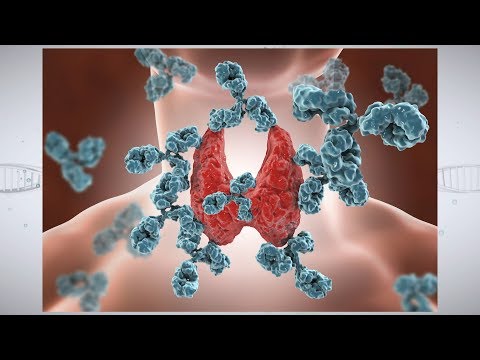
An autoimmune disease, when the body interprets components of the thyroid glands as threats and makes antibodies that attack the cells to destroy. The thyroid then cannot make enough of the thyroid hormone.
It most commonly presents as hypothyroidism with or without a goiter.
(Risk factors)
• female: 7 times more likely than male. It sometimes occurs during pregnancy.
• middle age: Most cases occur in 40-60 years of age.
• heredity: The disease tends to run in families. But no gene has been found that carries it.
• having other autoimmune diseases
• living in iodine-sufficient areas
(Symptoms)
• goiter
• hypothyroidism
• hyperthyroidism
(Diagnosis)
• presenting symptoms
• physical exam, including a neck exam
• plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration
• thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb): An immunoglobulin G, a conventional marker for thyroid autoimmunity. Less useful than TPOAb for predicting thyroid dysfunction.
• thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb): A type of thyroid antibody. Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid, that oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroid hormones (T3, T4).
• ultrasound: Obtain images to evaluate the size of the thyroid, find the presence of nodules, or provide clues for other thyroid conditions. It looks lumpy bumpy for diffuse vascularity and pseudo nodules (not real thyroid nodules but ultrasound artifacts).
(Treatment)
• levothyroxine therapy: An oral medication structured like endogenous T4, administered on a consistent schedule. It can be dosed based upon weight and adjusted based upon each patient. For example, the dose may be lowered for elderly patients or patients with certain cardiac conditions, but should be increased in pregnant patients.
• combination therapy with levothyroxine and liothyronine: Medication with endogenous T4 and synthetic T3.
• thyroidectomy: A surgery, not for the initial choice. Only for patients who are experiencing significant pressure symptoms, cosmetic concerns, or have nodules present on ultrasound.
An autoimmune disease, when the body interprets components of the thyroid glands as threats and makes antibodies that attack the cells to destroy. The thyroid then cannot make enough of the thyroid hormone.
It most commonly presents as hypothyroidism with or without a goiter.
(Risk factors)
• female: 7 times more likely than male. It sometimes occurs during pregnancy.
• middle age: Most cases occur in 40-60 years of age.
• heredity: The disease tends to run in families. But no gene has been found that carries it.
• having other autoimmune diseases
• living in iodine-sufficient areas
(Symptoms)
• goiter
• hypothyroidism
• hyperthyroidism
(Diagnosis)
• presenting symptoms
• physical exam, including a neck exam
• plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration
• thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb): An immunoglobulin G, a conventional marker for thyroid autoimmunity. Less useful than TPOAb for predicting thyroid dysfunction.
• thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb): A type of thyroid antibody. Thyroid peroxidase is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid, that oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroid hormones (T3, T4).
• ultrasound: Obtain images to evaluate the size of the thyroid, find the presence of nodules, or provide clues for other thyroid conditions. It looks lumpy bumpy for diffuse vascularity and pseudo nodules (not real thyroid nodules but ultrasound artifacts).
(Treatment)
• levothyroxine therapy: An oral medication structured like endogenous T4, administered on a consistent schedule. It can be dosed based upon weight and adjusted based upon each patient. For example, the dose may be lowered for elderly patients or patients with certain cardiac conditions, but should be increased in pregnant patients.
• combination therapy with levothyroxine and liothyronine: Medication with endogenous T4 and synthetic T3.
• thyroidectomy: A surgery, not for the initial choice. Only for patients who are experiencing significant pressure symptoms, cosmetic concerns, or have nodules present on ultrasound.
 0:20:11
0:20:11
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:21:47
0:21:47
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:49:42
0:49:42
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 1:22:13
1:22:13
 1:06:59
1:06:59
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:37
0:09:37
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:15:02
0:15:02
 0:16:28
0:16:28
 1:05:21
1:05:21
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:17:37
0:17:37
 0:35:02
0:35:02
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:00:57
0:00:57