filmov
tv
Logic 101 (#16): Double Negation

Показать описание
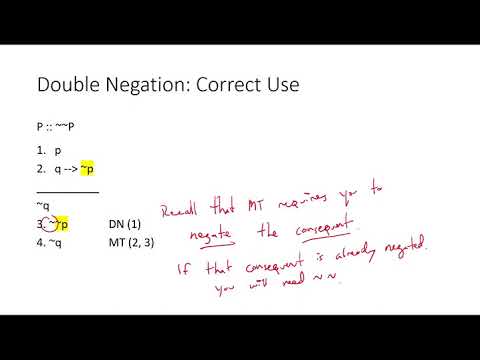
This lecture begins our unit on replacement rules. Replacement rules allow us to freely transition between two logically identical expressions. This means we can erase complicated expressions and use simpler ones instead.
Here, the double negation rule says we can replace ~~p with just p, where p is a simple sentence or compound expression.
Logic 101 (#16): Double Negation
Propositional Logic: Double Negation
Verify the Double Negative Property ~(~p) = p by Constructing a Truth Table
Intro to Logic: Sample derivation - double negation
Propositional Logic 5: Double Negation
the double-negation rule
A Shortcut for Intuitionistic Double-Negation | Attic Philosophy
Propositional Logic 5: Double Negation
3.3.2 Rule 9 Double Negation
Intro to Formal Logic 15: Double Negation
Derivation with Double Negation
Intro to Logic - Negation & Double Negation
Intro To Logic: Negations and Double Negation (DN)
Double Negatives | Spanish In 60 Seconds
3 Double Negation Symbolization
Double Negation law with proof and Example...Enjoy the fun
Logic 101 (#5): Negation
MATH 201: DeMorgan’s and double negation
Dr. Sahar Joakim, What is double negation?
Conditional Statements: if p then q
Double negation - Part 1
Logic - Part 4 - Double Negation, DeMorgan's Laws, and Biconditionals
How Does the Double Negation Law Work in Boolean Algebra #Shorts
Geoffrey Nunberg - Double Negatives
Комментарии
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:07:56
0:07:56
 0:01:12
0:01:12
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:07:09
0:07:09
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:28:28
0:28:28
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:01:18
0:01:18