filmov
tv
Transport Across Cell Membranes: Active Transport | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel

Показать описание
The key points covered of this video include:
1. Active Transport
2. The Process of Active Transport
Introduction to Active Transport
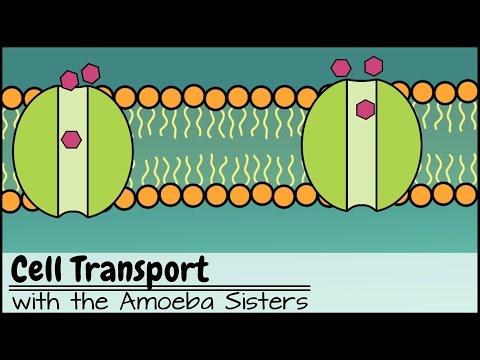
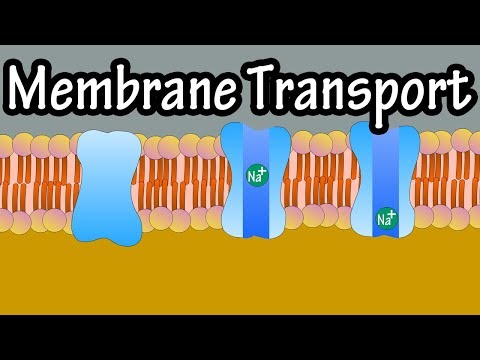
So far we have studied how substances can be passively transported into or out of cells by different types of diffusion. These processes allow substances to enter or leave cells down a concentration gradient without the cell expanding energy. However, sometimes cells need to transport substances into or out of cells against the concentration gradient. This is not able to passively occur a result of the natural motion of particles. Cells must instead use specific carrier proteins to pump a substance across the membrane - it is a selective process. This process requires energy in the form of ATP so it is known as active transport. Active transport is the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration across a cell membrane, using ATP and protein carriers.
The Process of Active Transport
In order to active transport to occur, the particle must bind to a specific site in the carrier protein. On the inside of the cell, ATP also binds to the carrier protein. The ATP is then hydrolysed to ADP and Pi which causes the carrier protein to change conformation (shape). The carrier protein is now open to the other side of the membrane and the particle is released. The phosphate molecule is then released from the carrier protein, which causes the carrier protein to return to its original shape.
Summary
Active transport is the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration across a cell membrane
Active transport requires ATP and the use of carrier proteins
ATP directly binds to carrier proteins and is hydrolysed to ADP and Pi, causing the carrier protein to change shape
This allows carrier proteins to transport particles against the concentration gradient
Комментарии
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 1:23:22
1:23:22
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:02:32
0:02:32
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:31:02
0:31:02
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:13:55
0:13:55
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:21:59
0:21:59
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 1:12:02
1:12:02