filmov
tv
Cell Membrane Transport - Transport Across A Membrane - How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane
Показать описание
In this video we discuss the different ways how substances transport across a cell membrane, including facilitated diffusion, channel mediated diffusion, carrier mediated diffusion, simple diffusion, passive transport and active transport.
Transcript/Notes (partial)
Substances move into and out of a cell through several different processes called membrane transport. There are two main processes, passive transport processes and active transport processes. The main difference between the two is that passive processes do not require energy expenditure and active processes do require cells to expend energy.
Lets start by looking at the passive processes, which include simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from where it has a high concentration to where it has a low concentration, or the tendency of a substance to spread out evenly over a given space.
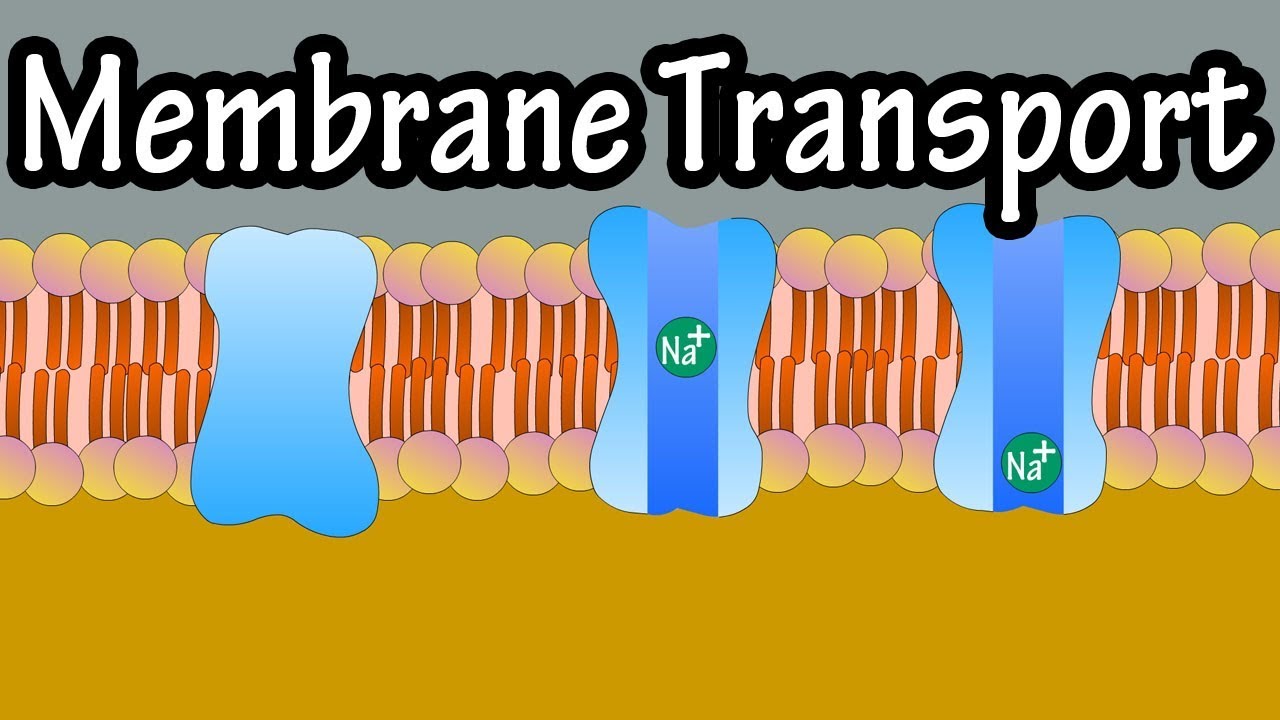
Simple diffusion occurs with solutes that are small and non polar. By being non polar they can move in between the phosphoipid molecules that form the plasma membrane because the interior region of the membrane is non polar. Some of the materials that move by simple diffusion include the gases O2, CO2, and small fatty acids. So, if there is a higher concentration of oxygen O2 molecules outside of a cell, they can move down the concentration gradient, across the membrane without assistance, and into the cell as long as the concentration gradient exists.
The second type of diffusion is facilitated diffusion. This applies to solutes that are small and either charged or polar. Because these solutes are polar, the non polar phospholipid bilayer blocks them from passing through the membrane and into or out of the cell by simple diffusion. However, they can pass into and out of the cell with the assistance of plasma membrane proteins through a process called facilitated diffusion. There are two types of facilitated diffusion, channel mediated diffusion and carrier mediated diffusion. The difference between the two is the type of transport protein used to move the substance across the membrane.
Channel mediated diffusion is when a ion, which is a charged particle where its total number of electrons does not equal its total number of protons giving it a positive or negative charge, moves across the membrane through a water filled protein channel. Each protein channel is typically specific for one type of ion, and there are two types of channels, a leak channel, which is continuously open, and a gated channel, which only opens due to a stimulus, and only stays open for a fraction of a second.
Carrier mediated diffusion involves the movement of polar molecules such as simple sugars or simple carbohydrates and amino acids across the membrane. This is accomplished by a carrier protein, which actually changes shape in the process. For instance glucose binds to a carrier protein, which changes shape and moves the glucose molecule to the other side of the membrane.
Now for osmosis. Osmosis is the passive movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane. This occurs when there is a difference in concentration of water on either side of the membrane. This can happen in one of two ways, water can slip between the phospholipid molecules that make up the plasma membrane, or through integral protein water channels that are called aquaporins.
Now lets look at active processes. As stated earlier, active processes require the use of cellular energy for membrane transport. There are two types of active processes, active transport and vesicular transport. Active transport is the movement of a solute against its concentration gradient, or going from an area of low concentration to a place of higher concentration. Vesicular transport is the transport of large substances across the plasma membrane by a vesicle, which is a membrane bound sac filled with materials.
Active transport has two types, primary active transport and secondary active transport.
In primary active transport cellular protein pumps called ion pumps move ions across the membrane, against their concentration gradient.
Timestamps
0:00 The structure of cell membranes
0:42 The 2 main membrane transport processes (passive and active)
1:12 What is diffusion?
2:11 Simple diffusion
3:05 Facilitated diffusion
3:44 Channel mediated diffusion
4:29 Carrier mediated diffusion
4:51 What is osmosis?
5:49 Active processes
6:01 Active transport
6:12 Vesicular transport
6:28 Primary active transport
7:27 Secondary active transport
8:37 The 2 types of vesicular transport
8:53 Exocytosis
9:23 Endocytosis
Transcript/Notes (partial)
Substances move into and out of a cell through several different processes called membrane transport. There are two main processes, passive transport processes and active transport processes. The main difference between the two is that passive processes do not require energy expenditure and active processes do require cells to expend energy.
Lets start by looking at the passive processes, which include simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from where it has a high concentration to where it has a low concentration, or the tendency of a substance to spread out evenly over a given space.
Simple diffusion occurs with solutes that are small and non polar. By being non polar they can move in between the phosphoipid molecules that form the plasma membrane because the interior region of the membrane is non polar. Some of the materials that move by simple diffusion include the gases O2, CO2, and small fatty acids. So, if there is a higher concentration of oxygen O2 molecules outside of a cell, they can move down the concentration gradient, across the membrane without assistance, and into the cell as long as the concentration gradient exists.
The second type of diffusion is facilitated diffusion. This applies to solutes that are small and either charged or polar. Because these solutes are polar, the non polar phospholipid bilayer blocks them from passing through the membrane and into or out of the cell by simple diffusion. However, they can pass into and out of the cell with the assistance of plasma membrane proteins through a process called facilitated diffusion. There are two types of facilitated diffusion, channel mediated diffusion and carrier mediated diffusion. The difference between the two is the type of transport protein used to move the substance across the membrane.
Channel mediated diffusion is when a ion, which is a charged particle where its total number of electrons does not equal its total number of protons giving it a positive or negative charge, moves across the membrane through a water filled protein channel. Each protein channel is typically specific for one type of ion, and there are two types of channels, a leak channel, which is continuously open, and a gated channel, which only opens due to a stimulus, and only stays open for a fraction of a second.
Carrier mediated diffusion involves the movement of polar molecules such as simple sugars or simple carbohydrates and amino acids across the membrane. This is accomplished by a carrier protein, which actually changes shape in the process. For instance glucose binds to a carrier protein, which changes shape and moves the glucose molecule to the other side of the membrane.
Now for osmosis. Osmosis is the passive movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane. This occurs when there is a difference in concentration of water on either side of the membrane. This can happen in one of two ways, water can slip between the phospholipid molecules that make up the plasma membrane, or through integral protein water channels that are called aquaporins.
Now lets look at active processes. As stated earlier, active processes require the use of cellular energy for membrane transport. There are two types of active processes, active transport and vesicular transport. Active transport is the movement of a solute against its concentration gradient, or going from an area of low concentration to a place of higher concentration. Vesicular transport is the transport of large substances across the plasma membrane by a vesicle, which is a membrane bound sac filled with materials.
Active transport has two types, primary active transport and secondary active transport.
In primary active transport cellular protein pumps called ion pumps move ions across the membrane, against their concentration gradient.
Timestamps
0:00 The structure of cell membranes
0:42 The 2 main membrane transport processes (passive and active)
1:12 What is diffusion?
2:11 Simple diffusion
3:05 Facilitated diffusion
3:44 Channel mediated diffusion
4:29 Carrier mediated diffusion
4:51 What is osmosis?
5:49 Active processes
6:01 Active transport
6:12 Vesicular transport
6:28 Primary active transport
7:27 Secondary active transport
8:37 The 2 types of vesicular transport
8:53 Exocytosis
9:23 Endocytosis
Комментарии
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:13:55
0:13:55
 1:23:22
1:23:22
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:44:11
0:44:11
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:07:43
0:07:43
 1:12:02
1:12:02
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:52:48
0:52:48
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 0:00:45
0:00:45