filmov
tv
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.4: Hydrogen Atom: Radiative Atomic Transitions

Показать описание
Table of Contents:
00:09 Lecture 6.4: Radiative Atomic Transitions
01:12 Radiative Transitions between discrete energy levels
02:15 Transition between two quantum states produces an EM wave?
03:21 How might a wavefunction change with time?
04:42 Multiply both sides by :
05:47 Why is a photon emitted?
08:28 B. What is
11:45 Two choices?
13:39 Working it Out
15:39 Untitled: Slide 10
16:48 Untitled: Slide 11
17:54 Summary – in One Slide
21:37 What does it mean?
23:51 Up next
Purdue PHYS 342 provides an introduction to the physical principles underlying topics in Modern Physics. This course is intended to provide engineering undergraduate students with a firm base from which they can extend their understanding of the quantum world.
00:09 Lecture 6.4: Radiative Atomic Transitions
01:12 Radiative Transitions between discrete energy levels
02:15 Transition between two quantum states produces an EM wave?
03:21 How might a wavefunction change with time?
04:42 Multiply both sides by :
05:47 Why is a photon emitted?
08:28 B. What is
11:45 Two choices?
13:39 Working it Out
15:39 Untitled: Slide 10
16:48 Untitled: Slide 11
17:54 Summary – in One Slide
21:37 What does it mean?
23:51 Up next
Purdue PHYS 342 provides an introduction to the physical principles underlying topics in Modern Physics. This course is intended to provide engineering undergraduate students with a firm base from which they can extend their understanding of the quantum world.
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.6: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: Energy Eigenvalues
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.4: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: Separation of Variables
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.3: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: 3D Schrödinger's Equa...
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.5: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: Eigenfunctions
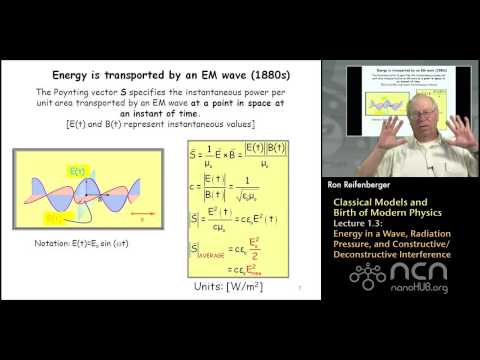
Purdue PHYS 342 L1.3: Classical Models: Energy in a Wave, Radiation Pressure, and Interference
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.2: Hydrogen Atom: Angular Momentum Operators
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.3: Hydrogen Atom: Vector Model of Angular Momentum
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.1: Hydrogen Atom: The Radial Probability Density
Purdue PHYS 342 L14.1: Relativistic Kinematics: Compton Scattering
Purdue PHYS 342 L15.1: Nuclear Structure and Decay: Nuclear Characteristics
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.5: Hydrogen Atom: Optical Absorption
Purdue PHYS 342 L2.2: Schrödinger Equation in 1D: 1D Equation to Describe de Broglie 'Matter Wa...
Purdue PHYS 342 L15.2: Nuclear Structure and Decay: The Strong Force
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.2: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: 2D Density of States
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.4: Hydrogen Atom: Radiative Atomic Transitions
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L5.1: Schrödinger Equation and Hydrogen: 2D Schrödinger's Equat...
Purdue PHYS 342 L15.3: Nuclear Structure and Decay: Nuclear Shell Structure
Purdue PHYS 342 L7.1: Pauli's Exclusion Principle: Orbital Magnetic Moments
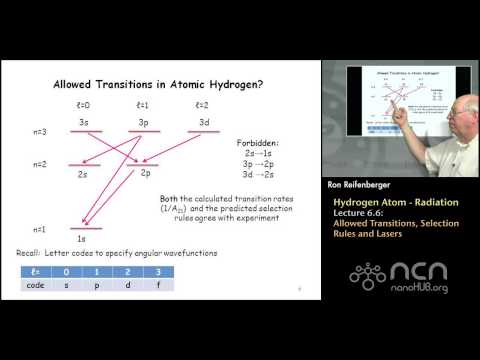
Purdue PHYS 342: Modern Physics L6.6: Hydrogen Atom: Allowed Transitions, Selection Rules and Lasers
Purdue PHYS 342 L4.1: Heisenberg's Uncertainty: Scattering of Matter-Waves from a Step Potentia...
Purdue PHYS 342 L15.4: Nuclear Structure and Decay: Nuclear Decay
Purdue PHYS 342 L11.1: Electron States in Periodic Solids: Free Electron Model
Purdue PHYS 342 L7.6: Pauli's Exclusion Principle: Many-Particle Wavefunctions
Purdue PHYS 342 L1.6: Classical Models: Compton Effect
Комментарии
 0:30:21
0:30:21
 0:18:56
0:18:56
 0:32:27
0:32:27
 0:27:36
0:27:36
 0:28:31
0:28:31
 0:23:19
0:23:19
 0:25:33
0:25:33
 0:26:55
0:26:55
 0:23:06
0:23:06
 0:30:24
0:30:24
 0:31:25
0:31:25
 0:19:52
0:19:52
 0:30:08
0:30:08
 0:19:16
0:19:16
 0:24:26
0:24:26
 0:29:31
0:29:31
 0:17:27
0:17:27
 0:32:39
0:32:39
 0:22:48
0:22:48
 0:26:23
0:26:23
 0:23:18
0:23:18
 0:23:15
0:23:15
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:22:10
0:22:10