filmov
tv
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Explained

Показать описание
Dr D. Bulte from Oxford University's FMRIB (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain) centre explains the theory underlying today's modern MRI scanners and outlines the work of the FMRIB centre.
If you are interested in the field of Biomedical Sciences, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging, please click on the link below to visit Oxford University's Biomedical Sciences undergraduate course.
This video was produced by Oxford Medical Illustration -- a non-profit making NHS department. For more information please click on the link below:
If you are interested in the field of Biomedical Sciences, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging, please click on the link below to visit Oxford University's Biomedical Sciences undergraduate course.
This video was produced by Oxford Medical Illustration -- a non-profit making NHS department. For more information please click on the link below:
How does an MRI machine work?
How does an MRI work? | MRI basics explained | Animation
MRI explained: How does it work?
MRI Physics | Magnetic Resonance and Spin Echo Sequences - Johns Hopkins Radiology
The Insane Engineering of MRI Machines
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Explained
How Does an MRI Scan Work?
MRI Basics Part 1
The Ugly Truth About MRI Physics | MRI Physics Course Lecture 16
2-Minute Neuroscience: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
MRI physics overview | MRI Physics Course | Radiology Physics Course #1
How does an MRI work?
MRIs Are Insane
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) explained | Neuroscience Methods 101
What is an MRI?
Introduction to Radiology: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
What happens during an MRI examination?
Understanding MRI: What is functional MRI (fMRI)?
What is an MRI? | Ohio State Medical Center
How MRI Works - Part 1 - NMR Basics
T1 vs T2 weighted MRI images: How to tell the difference
Introduction to MRI: Basics 1 - How we get Signal
How does an MRI machine work?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Комментарии
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:17:53
0:17:53
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:21:34
0:21:34
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:23:13
0:23:13
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:01:00
0:01:00
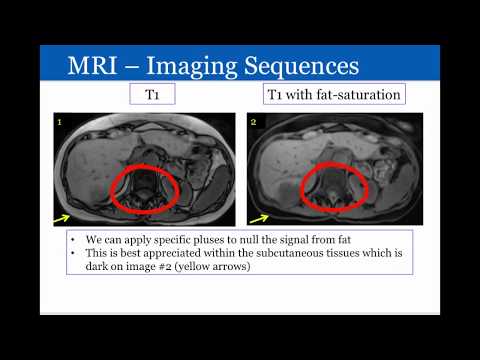 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:42:44
0:42:44
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:01:17
0:01:17