filmov
tv
Big Data on Spark | Tutorial for Beginners [Part 5] | More on Spark | Great Learning

Показать описание
Today, we’re surrounded by data. People upload videos, take pictures on their cell phones, text friends, update their Facebook status, leave comments around the web, click on ads, and so forth. Machines, too, are generating and keeping more and more data.
Existing tools were becoming inadequate to process such large data sets.
Spark--
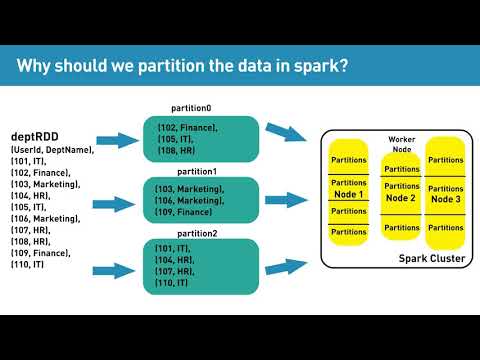
A new framework was proposed which is called Spark that supports these applications while retaining the scalability and fault tolerance of MapReduce(Hadoop). To achieve these goals, Spark introduces an abstraction called resilient distributed datasets (RDDs). An RDD is a read-only collection of objects partitioned across a set of machines that can be rebuilt if a partition is lost. Spark can outperform Hadoop by 10x in iterative machine learning jobs, and can be used to interactively query a very large dataset with sub-second response time.
About the Speaker: Raghu Raman A V
Raghu is a Big Data and AWS expert with over a decade of training and consulting experience in AWS, Apache Hadoop Ecosystem including Apache Spark.
He has worked with global customers like IBM, Capgemini, HCL, Wipro to name a few as well as Bay Area startups in the US.
#GreatLearning #BigData #SparkTutorial
About Great Learning:
- Great Learning is an online and hybrid learning company that offers high-quality, impactful, and industry-relevant programs to working professionals like you. These programs help you master data-driven decision-making regardless of the sector or function you work in and accelerate your career in high growth areas like Data Science, Big Data Analytics, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence & more.
For more updates on courses and tips follow us on:
Great Learning has collaborated with the University of Texas at Austin for the PG Program in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning and with UT Austin McCombs School of Business for the PG Program in Analytics and Business Intelligence.
Комментарии
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:15:40
0:15:40
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:42:17
0:42:17
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 7:15:32
7:15:32
 1:49:02
1:49:02
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 1:00:00
1:00:00
 3:01:19
3:01:19
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:48:54
0:48:54
 0:28:21
0:28:21
 0:06:26
0:06:26