filmov
tv
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra: Spacetime.

Показать описание
In this lesson we continue our reading of an excellent paper on Geometric Algebra and spacetime algebra. The paper can be found here:
We will cover section 3.1 and begin section 3.2. This material includes our first expansion of the vector space of spacetime to include objects that are NOT the familiar 4-vectors of relativity. Also, we spend some time trying to clear up ambiguous usage of the word "vector" which often appears whenever we try to discuss vector spaces in a purely mathematical way.
The software I usually use to produce the lectures is:
We will cover section 3.1 and begin section 3.2. This material includes our first expansion of the vector space of spacetime to include objects that are NOT the familiar 4-vectors of relativity. Also, we spend some time trying to clear up ambiguous usage of the word "vector" which often appears whenever we try to discuss vector spaces in a purely mathematical way.
The software I usually use to produce the lectures is:
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra: Spacetime.
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra: Introduction and Motivation
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 23 Spacetime Split
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 8 Better notation for basis vectors
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 11 Reversion and Inversion
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 9: Multivector Structure
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 15: Complex Structure
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 28: Relativistic Physics Intro
QED Prerequisites: Geometric Algebra - Maxwell's Equations
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 6 - Multivector Products
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 5- Multivectors
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 7 - Multivector Addition
QED Prerequisites 27: A Lorentz Boost using the Spacetime Algebra
QED Prerequisites -Geometric Algebra 12: Reciprocal basis, calculation of components
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 29 - Relativistic velocity
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 10: Bivector-vector products
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 4: The antisymmetric part
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 13 Tensors
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 14: The Pseudoscalar
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 17 - Bivector products
QED Prerequisites Geomemtric Algebra 22 Relative Vectors
QED Prerequisites 30 Geometric Algebra - SPINORS
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 16: Canonical Bivectors
QED Prerequisites Geometric Algebra 26 The Lorentz Group
Комментарии
 0:37:21
0:37:21
 0:38:31
0:38:31
 0:50:23
0:50:23
 0:55:15
0:55:15
 0:38:20
0:38:20
 0:58:11
0:58:11
 0:32:18
0:32:18
 0:58:55
0:58:55
 1:13:35
1:13:35
 0:58:35
0:58:35
 0:56:36
0:56:36
 0:31:04
0:31:04
 0:46:48
0:46:48
 0:44:10
0:44:10
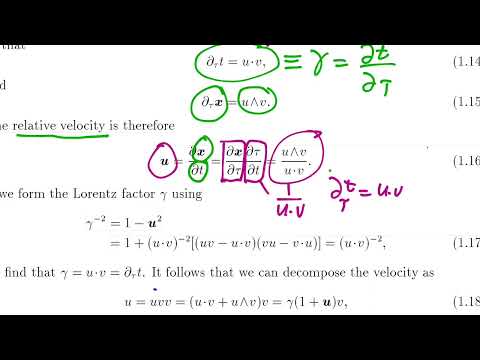 0:53:38
0:53:38
 0:54:02
0:54:02
 0:39:51
0:39:51
 0:39:36
0:39:36
 0:47:46
0:47:46
 0:53:30
0:53:30
 0:52:06
0:52:06
 1:00:51
1:00:51
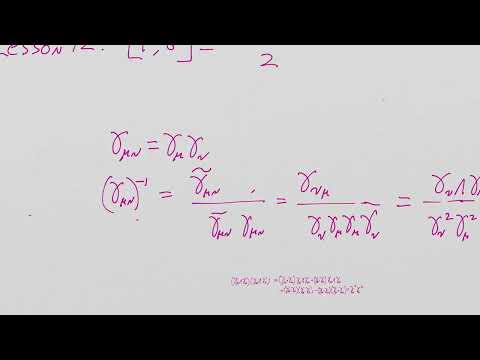 0:49:30
0:49:30
 0:44:42
0:44:42