filmov
tv
Deep Vein Thrombosis & Pulmonary Embolism Video – Brigham and Women’s Hospital

Показать описание
Samuel Goldhaber, MD, Director, Thrombosis Research Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, discusses deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
A deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot, usually in the pelvic or deep leg veins, occasionally in the upper extremity veins which is a potentially major medical problem. If the blood clot breaks off, its natural route of travel is through the heart and into the lungs, where it can cause a potentially deadly pulmonary embolism.
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that is lodging in the pulmonary arteries, choking off the blood supply to the heart. It can cause right heart failure, collapse, and at times sudden death.
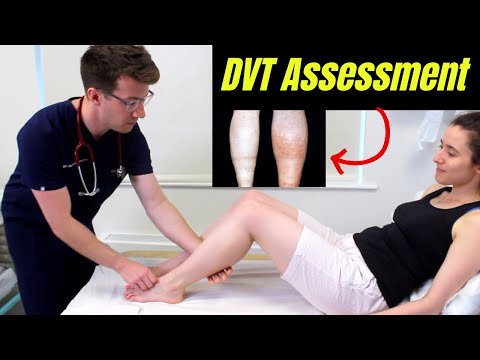
The primary symptom of deep vein thrombosis is a Charlie horse in the calf that persists. Many people dismiss this as a muscle ache and don't realize it might be the sign of a serious condition that requires diagnosis and treatment.
Unexplained breathlessness is the primary symptom of pulmonary embolism but it can also present as unexplained fainting or anxiety. The symptoms can also mimic pneumonia or heart attack. The symptoms can be very nonspecific at times making difficult to diagnose accurately.
The primary treatment for DVT and pulmonary embolism is anticoagulation or blood thinning. Currently, there are several FDA-approved novel oral anticoagulants for the treatment of DVT or PE.
The best way to prevent DVT is with a heart-healthy lifestyle and plenty of daily exercise. The American Heart Association recommends at least 30 minutes of exercise daily for at least six days per week.
Learn more about deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism at Brigham and Women’s Hospital:
A deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot, usually in the pelvic or deep leg veins, occasionally in the upper extremity veins which is a potentially major medical problem. If the blood clot breaks off, its natural route of travel is through the heart and into the lungs, where it can cause a potentially deadly pulmonary embolism.
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that is lodging in the pulmonary arteries, choking off the blood supply to the heart. It can cause right heart failure, collapse, and at times sudden death.
The primary symptom of deep vein thrombosis is a Charlie horse in the calf that persists. Many people dismiss this as a muscle ache and don't realize it might be the sign of a serious condition that requires diagnosis and treatment.
Unexplained breathlessness is the primary symptom of pulmonary embolism but it can also present as unexplained fainting or anxiety. The symptoms can also mimic pneumonia or heart attack. The symptoms can be very nonspecific at times making difficult to diagnose accurately.
The primary treatment for DVT and pulmonary embolism is anticoagulation or blood thinning. Currently, there are several FDA-approved novel oral anticoagulants for the treatment of DVT or PE.
The best way to prevent DVT is with a heart-healthy lifestyle and plenty of daily exercise. The American Heart Association recommends at least 30 minutes of exercise daily for at least six days per week.
Learn more about deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism at Brigham and Women’s Hospital:
Комментарии
 0:22:43
0:22:43
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:12:18
0:12:18
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:22:01
0:22:01
 0:28:43
0:28:43
 0:09:45
0:09:45
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:14:44
0:14:44
 0:10:48
0:10:48
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:14:56
0:14:56