filmov
tv
Conic Section Parabola Focus Directrix Latus-rectum Standard Form and Transformation Equation

Показать описание
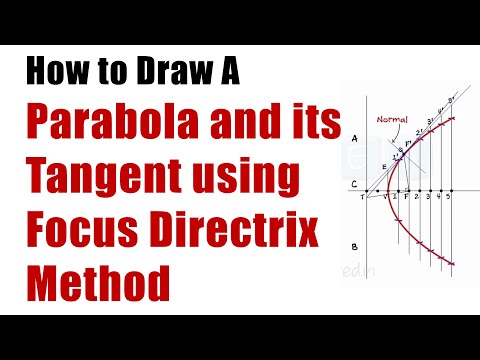
Parabola: Definitions
Conic section with locus of points which moves in such a way that its distances from a fixed point (focus) is exactly equal to its distance from a fixed line (directrix), all being in the same plane.
#PreCalculus #Locus #Focus #Vertices #ConicSection #Ellipse #AnilKumarMath #Parabola #Circle #Hyperbola
Focus: Point about which the rays reflected from the surface of the curve converges
Directrix: Fixed straight line
Eccentricity: Constant ratio to the distance from the point to the focus and directrix. Eccentricity, e, is one for parabola.
Axis: Straight line through focus and perpendicular to directrix
Vertex: Point of intersection of the curve and axis
Parabola: Chords
A chord connects two points on the curve.
Double Ordinate is a chord perpendicular to the axis.
Latus-rectum is the double ordinate passing through the focus.
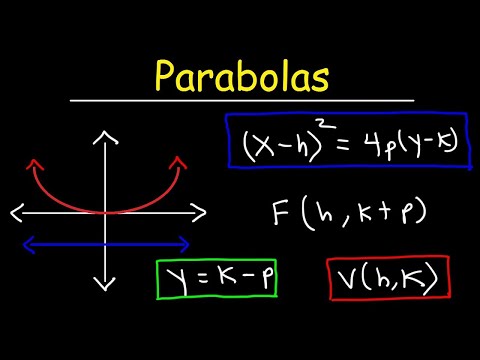
Standard Form of Parabola
Orientation: opens right
Vertex: V(0,0)
Focus: F(p,0)
Axis: y=0
Directrix: x=-p
Latus-rectum length: LL'=4p
Focal distance: PF=p+x
Equation: y^2=4px or x=1/4p y^2
Vertical Stretch: a=1/4p
Transformational Form of Parabola
A parabola is the set of points whose distance from a focus is same as that from directrix. Vertex is halfway between focus and directrix.
Parabola Up:
Vertex(h,k),
Focus(h,k+p),
directrix:y=k-p
y=1/4p (x-h)^2+k,a=1/4p
Parabola Sides:
Vertex(h,k),
Focus(h+p,k),
directrix:x=h-p
x=1/4p (y-k)^2+h,a=1/4p
Conic section with locus of points which moves in such a way that its distances from a fixed point (focus) is exactly equal to its distance from a fixed line (directrix), all being in the same plane.
#PreCalculus #Locus #Focus #Vertices #ConicSection #Ellipse #AnilKumarMath #Parabola #Circle #Hyperbola
Focus: Point about which the rays reflected from the surface of the curve converges
Directrix: Fixed straight line
Eccentricity: Constant ratio to the distance from the point to the focus and directrix. Eccentricity, e, is one for parabola.
Axis: Straight line through focus and perpendicular to directrix
Vertex: Point of intersection of the curve and axis
Parabola: Chords
A chord connects two points on the curve.
Double Ordinate is a chord perpendicular to the axis.
Latus-rectum is the double ordinate passing through the focus.
Standard Form of Parabola
Orientation: opens right
Vertex: V(0,0)
Focus: F(p,0)
Axis: y=0
Directrix: x=-p
Latus-rectum length: LL'=4p
Focal distance: PF=p+x
Equation: y^2=4px or x=1/4p y^2
Vertical Stretch: a=1/4p
Transformational Form of Parabola
A parabola is the set of points whose distance from a focus is same as that from directrix. Vertex is halfway between focus and directrix.
Parabola Up:
Vertex(h,k),
Focus(h,k+p),
directrix:y=k-p
y=1/4p (x-h)^2+k,a=1/4p
Parabola Sides:
Vertex(h,k),
Focus(h+p,k),
directrix:x=h-p
x=1/4p (y-k)^2+h,a=1/4p
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:34:54
0:34:54
 1:00:16
1:00:16
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:09:45
0:09:45
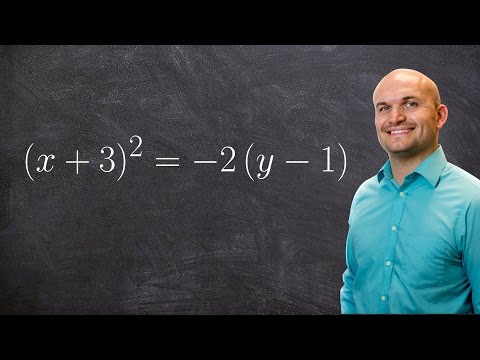 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:10:31
0:10:31
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:13:56
0:13:56
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:58:17
0:58:17