filmov
tv
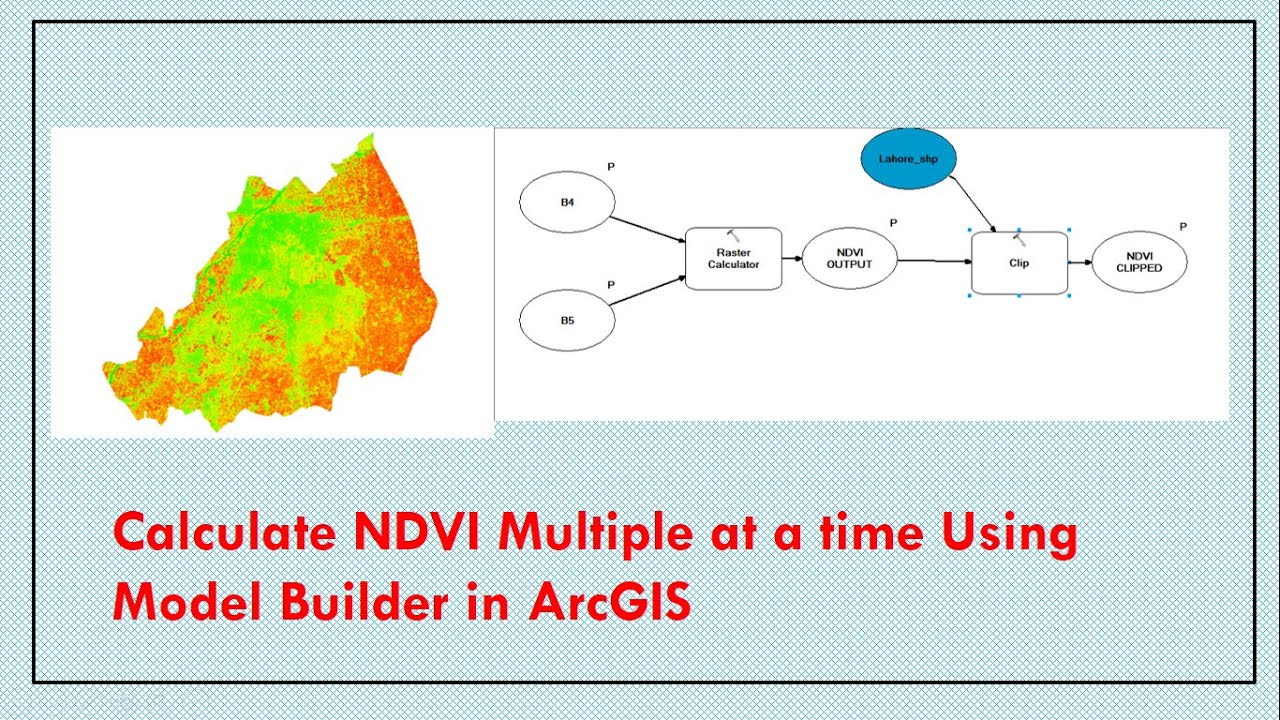
Calculate NDVI multiple at a time using Model Builder in ArcGIS
Показать описание
In This Tutorial, i will present how to calculate NDVI multiple at a time of any area at different time period using odel Builder in ArcGIS
As one of the most popular vegetation indices, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) is a valuable way to understand vegetation health and land use remotely.
Satellite sensors in space measure wavelengths of light absorbed and reflected by green plants. They are an excellent source of spectral signature data for NDVI analysis.
The NDVI formula combines the information available in the red and NIR bands into a single and representative value.
It does this by subtracting the reflectance in the red spectral band from that in the NIR. Then, it divides this by the sum of the NIR and red reflectance.
The value of the NDVI will always fall between -1 and +1.
Values between -1 and 0 indicate dead plants, or inorganic objects such as stones, roads, and houses.
NDVI values for live plants range between 0 to 1, with 1 being the healthiest and 0 being the least healthy. A single value can be determined for every pixel in an image—ranging from an individual leaf to a 500-acre wheat field.
The NDVI index detects and quantifies the presence of live green vegetation using this reflected light in the visible and near-infrared bands.
Put simply, NDVI is an indicator of the vegetation greenness —the density and health—of each pixel in a satellite image.
#arcmap #arcgis #arcgistutorial #gis #ndvi #modelbuilder #landsat #remotesensing #ARCGIS
As one of the most popular vegetation indices, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) is a valuable way to understand vegetation health and land use remotely.
Satellite sensors in space measure wavelengths of light absorbed and reflected by green plants. They are an excellent source of spectral signature data for NDVI analysis.
The NDVI formula combines the information available in the red and NIR bands into a single and representative value.
It does this by subtracting the reflectance in the red spectral band from that in the NIR. Then, it divides this by the sum of the NIR and red reflectance.
The value of the NDVI will always fall between -1 and +1.
Values between -1 and 0 indicate dead plants, or inorganic objects such as stones, roads, and houses.
NDVI values for live plants range between 0 to 1, with 1 being the healthiest and 0 being the least healthy. A single value can be determined for every pixel in an image—ranging from an individual leaf to a 500-acre wheat field.
The NDVI index detects and quantifies the presence of live green vegetation using this reflected light in the visible and near-infrared bands.
Put simply, NDVI is an indicator of the vegetation greenness —the density and health—of each pixel in a satellite image.
#arcmap #arcgis #arcgistutorial #gis #ndvi #modelbuilder #landsat #remotesensing #ARCGIS
Комментарии
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:15:58
0:15:58
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:24:51
0:24:51
 0:18:10
0:18:10
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:21:25
0:21:25
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:09:40
0:09:40
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:25:18
0:25:18
 0:05:14
0:05:14