filmov
tv
Tutorial 2- What is Population And Sample And Sampling Techniques In Hindi?

Показать описание
A population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. A sample is the specific group that you will collect data from. The size of the sample is always less than the total size of the population.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please donate if you want to support the channel through GPay UPID,
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Recording Gears That I Use
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#krish #statsbusted
Connect with me here:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please donate if you want to support the channel through GPay UPID,
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Recording Gears That I Use
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#krish #statsbusted
Connect with me here:
Tutorial 2- What is Population And Sample And Sampling Techniques In Hindi?
Research Design: Defining your Population and Sampling Strategy | Scribbr 🎓
Tutorial 2: Parameter vs. Statistic and Population vs. Sample - Explained with Examples
Tutorial 5: Population vs Sample in Statistics| Data Science| Machine Learning
Sample and Population in Statistics | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures
Maths Tutorial: Samples and Populations (Statistics)
Population pyramids: Powerful predictors of the future - Kim Preshoff
2018 OHDSI Population-Level Estimation Tutorial (2 of 6)
Statistical inference I 2 marks fixed questions |
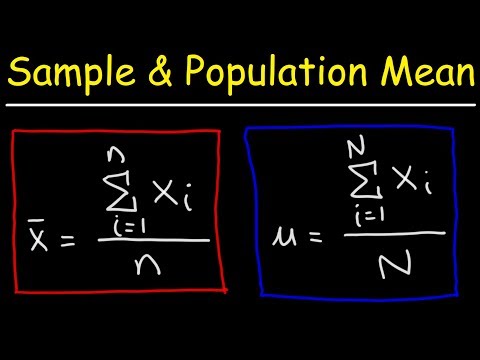
Sample Mean and Population Mean - Statistics
What Are The Types Of Sampling Techniques In Statistics - Random, Stratified, Cluster, Systematic
Populations and Samples (Intro Psych Tutorial #11)
2017 OHDSI Population Level Estimation Tutorial (2 of 7)
Victoria 3 - The 7 HUGE MISTAKES Everyone is Making! (Victoria 3 Tutorial)
Plus Two Biology | 10 Mark Sure Questions - Don't Miss it | Exam Winner
SONIC ➤ timelapse. Plastilina Tutorial. With Polymer Clay #shorts
What is Statistics? | Types of Statistics | Descriptive & Inferential Statistics | Acadgild
Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean
Hypothesis Testing - Difference of Two Means - Student's -Distribution & Normal Distributio...
TITLE SLIDES Tutorial in PowerPoint 😍#powerpoint #tutorial #presentation
Victoria 2 Tutorial 'Population and Industry'
#shorts Regression Slope Microsoft Excel Tutorial
DIY rainbow marker 🌈😍 #shorts #artist #art #diy #creative #tutorial #crafts #draw #craft #rainbow...
Dummynation Tutorial From An Expert
Комментарии
 0:15:54
0:15:54
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:22:09
0:22:09
 0:12:42
0:12:42
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:27:30
0:27:30
 0:17:01
0:17:01
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:18:36
0:18:36
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:12:22
0:12:22
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:34:37
0:34:37