filmov
tv
Degradation of Purine Nucleotides easy #purines #uricacid #biochemistry

Показать описание
Let's explore the process of uric acid formation from purines:
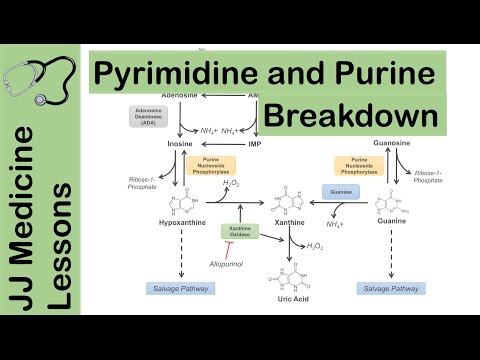
1. Purine Catabolism:
- Purines are chemical compounds found in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
- When nucleic acids are ingested in the diet, they are broken down into nucleotides by various enzymes.
- Nucleotides are further converted to nucleosides (base + ribose or deoxyribose).
- Nucleosides are then hydrolyzed by enzymes like Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase (PNP) to release the purine base and ribose-1-P.
- Notably, adenosine and deoxyadenosine are first converted to inosine by adenosine deaminase before being processed by PNP.
- The PNP products merge into xanthine through guanine deaminase and xanthine oxidase.
- Finally, xanthine is oxidized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase.
2. Clinical Significance:
- Hyperuricemia occurs when blood uric acid levels are elevated due to impaired excretion or overproduction of purines.
- High purine intake from foods like organ meats (liver), beef, fish, and alcohol can contribute to uric acid formation.
- Uric acid stones may form in the kidneys under certain conditions.
#purinecatabolismtrick #uricacidformationmadesimple #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimple #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimplevideo #uricacidformationmadesimpleand #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimpleandrew
1. Purine Catabolism:
- Purines are chemical compounds found in nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
- When nucleic acids are ingested in the diet, they are broken down into nucleotides by various enzymes.
- Nucleotides are further converted to nucleosides (base + ribose or deoxyribose).
- Nucleosides are then hydrolyzed by enzymes like Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase (PNP) to release the purine base and ribose-1-P.
- Notably, adenosine and deoxyadenosine are first converted to inosine by adenosine deaminase before being processed by PNP.
- The PNP products merge into xanthine through guanine deaminase and xanthine oxidase.
- Finally, xanthine is oxidized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase.
2. Clinical Significance:
- Hyperuricemia occurs when blood uric acid levels are elevated due to impaired excretion or overproduction of purines.
- High purine intake from foods like organ meats (liver), beef, fish, and alcohol can contribute to uric acid formation.
- Uric acid stones may form in the kidneys under certain conditions.
#purinecatabolismtrick #uricacidformationmadesimple #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimple #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimplevideo #uricacidformationmadesimpleand #purinecatabolismtrickuricacidformationmadesimpleandrew
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:44:10
0:44:10
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:06:36
0:06:36
 0:37:39
0:37:39
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:16:46
0:16:46
 0:27:20
0:27:20
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:08:39
0:08:39
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:00:10
0:00:10