filmov
tv
Hydrogen Bonding in Water | A Level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel

Показать описание
Our A-Level Chemistry Experts are here to help you ace A-Level Chemistry!
This week we are revising Hydrogen Bonding in Water
A-Level Chemistry can be tough but fortunately we’ve made this tutorial to help you score the A* you need for questions on everything to do with Hydrogen Bonding in Water.
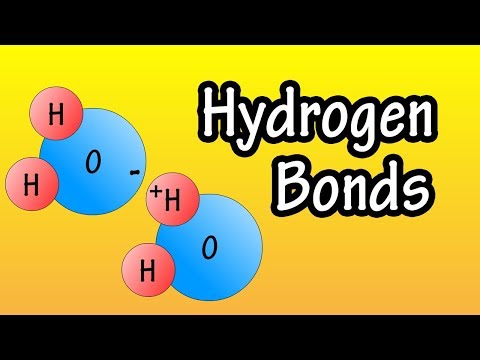
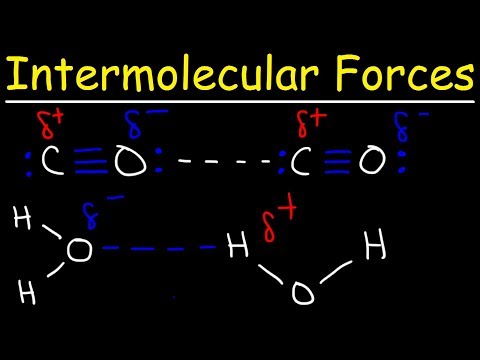
As we said in the previous chapter, hydrogen bonds are a special type of permanent dipole-dipole forces that form when hydrogen forms a covalent bond with a very electronegative element: either nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine. They are the strongest type of intermolecular force.
Water molecules are highly polarized molecules that are able to form an extensive network of hydrogen bonds. The lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom are attracted to the δ+ of the hydrogen in nearby water molecules. Each water molecule can form a total of 4 hydrogen bonds.
The extensive hydrogen bonding that occurs in water accounts for its anomalous physical properties.
If we compare the boiling points of Group 6 hydrides, we can see that those for water are significantly higher than would have been expected.
As we go down the group and number of electrons increases, so does the strength of London forces between molecules, so that boiling point increases. However, the strong hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules, overrides the effects of their weaker London forces. The same principle applies to melting points.
Surface tension refers to how strongly molecules are held to the surface of a liquid. As a result of hydrogen bonds which exert a strong downwards force on water molecules at the surface, water has a higher surface tension than most other liquids.
Viscosity is a measure of how resistant to flow a liquid is as a result of friction between its molecules. Due to the hydrogen bonds between them, water molecules are less capable to slide over each other so that water has a high viscosity.
In general, solids are denser than their liquids but for water, the density of solid ice is lower than the density of liquid water.
#ALevelChemistry #ALevelBiology #Biology #Chemistry #StudyMind
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:11:40
0:11:40
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:10:40
0:10:40