filmov
tv
Mechanism of action of opioids

Показать описание
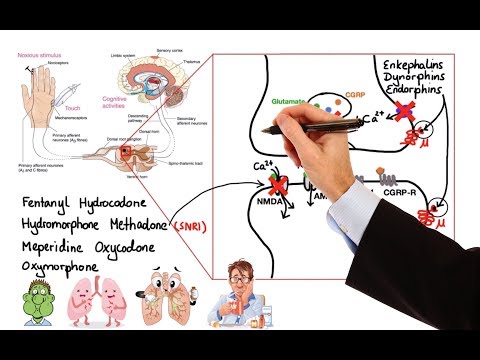
Opioid agonists produce analgesia by binding to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the brain and spinal cord regions involved in the transmission and modulation of pain
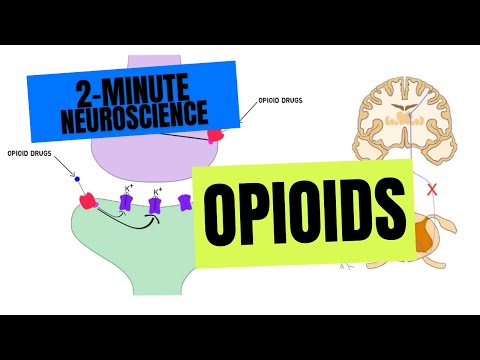
Opioid drugs mimic endogenous compounds: endorphins, enkephalins, and dynorphins that bind to opioid receptors.
Four opioid receptor types: mu (μ), kappa (κ), delta (δ), and sigma (σ) → GPCR → membrane hyperpolarization → blocks release/response of excitatory neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, substance P) → inhibits nociceptive neurons
Inhibition can occur at several points along pain pathway: periphery → afferent neurons → dorsal horn of spinal cord → secondary neuron
Agonist-antagonists (nalbuphine, butorphanol, and pentazocine) have less efficacy than full agonists (fentanyl)
Opioid drugs mimic endogenous compounds: endorphins, enkephalins, and dynorphins that bind to opioid receptors.
Four opioid receptor types: mu (μ), kappa (κ), delta (δ), and sigma (σ) → GPCR → membrane hyperpolarization → blocks release/response of excitatory neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, substance P) → inhibits nociceptive neurons
Inhibition can occur at several points along pain pathway: periphery → afferent neurons → dorsal horn of spinal cord → secondary neuron
Agonist-antagonists (nalbuphine, butorphanol, and pentazocine) have less efficacy than full agonists (fentanyl)
Opioid Mechanism of Action
2-Minute Neuroscience: Opioids
Opioids and Opiates
Pharmacology - OPIOIDS (MADE EASY)
Mechanism of action of opioids
2-Minute Neuroscience: Fentanyl
Opioid Analgesic Mechanism of Action | Mechanism of Action of Opioid Analgesic | Opioid Analgesics
Mechanism of Action of a Partial Opioid Agonist
Opioids Mechanism of Action
Opioid Antagonist= Mechanism of Action | Mechanism of Action of Opioid Analgesic Drugs | Animation
Opioid Mechanism of Action
Nursing School Notes on Opioids! | Pharmacology Help for Nursing Students
Analgesic Pathway | Endogenous Opioid System
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
Opioid Mechanism of Action
Pharmacodynamics of Medications for Opioid Use Disorder
2-Minute Neuroscience: Methadone
Pharmacology Analgesics - Opioids, NSAIDS, Tylenol - Nursing RN PN (MADE EASY)
Opioid Analgesics Made Easy!
Morphine Side Effects and Mechanism of Action | Opioid Analgesics
Opioid Analgesic & Its Antagonist (Part 04 Final) = Opioid Antagonist and It's Mechanism of...
Opioid Analgesic Mechanism of Action |Opioid Analgesics | #solutionpharmacy
Buprenorphine for Opioid Use Disorder
How do opioids cause dependency, and how the ANR treatment can help defeat it?
Комментарии
 0:05:16
0:05:16
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:09:26
0:09:26
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:09:26
0:09:26
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:17:04
0:17:04
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:00:56
0:00:56