filmov
tv
Dealing with nonlinear data: Polynomial regression and log transformations

Показать описание
Dealing with nonlinear data: Polynomial regression and log transformations
Polynomial regression
Handling Non-Linear Relationships with Polynomial Regression in Python
6. Polynomial Regression Explained | How to Model Non-Linear Data
How to fit non-linear equations in excel using solver
Polynomial (Nonlinear) Regression 1: Idea and Theory
Polynomial Linear Regression [ Explained ] | Non Linear Data | Machine Learning Algorithms
Best fit of non-linear equation + Polynomial regression
Sine and Cosine Function #brainboost #maths #mathematics #calculus #jesus #jee #jeemains
Statistical Thinking - Polynomial Regression and Non Linear Relationship
16. Polynomial Regression: Extending Linear Models for Nonlinear Relationships
10- Nonlinear & Polynomial Regression Explained | Applications & Differences from Linear Re...
Linear Least Squares to Solve Nonlinear Problems
Polynomial (Nonlinear) Regression 3: Polynomial Degree Selection
Why Linear Regression Fails: Polynomial Regression Explained
MS Excel: Performing Non-Linear Polynomial Regression in MS Excel Using Python and Scatter Charts
12 - Testing for a nonlinear trend (polynomial regression) in R
Polynomial Regression Model in Python: A Beginner's Guide to Machine Learning
What is Polynomial Regression in Machine Learning?
6-Polynomial Regression | Detailed Explanation on Polynomial Regression | ML for Non Tech
How do SVMs handle non-linear data? #machinelearning #datascience #aiexplained #shorts #svm
Lec 19: Non linear models and piecewise polynomial regression
Polynomial regression, general linear least squares method, non-linear regression
Spline Regression | Non Linear Model | Polynomial Regression
Комментарии
 0:14:50
0:14:50
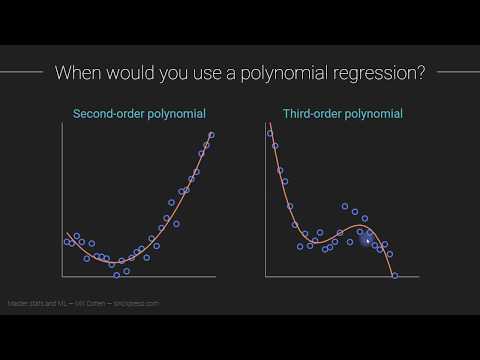 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:16:44
0:16:44
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:14:27
0:14:27
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:15:36
0:15:36
 0:07:08
0:07:08
 0:33:41
0:33:41
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:20:21
0:20:21
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:17:14
0:17:14
 0:12:52
0:12:52
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:26:43
0:26:43
 0:36:25
0:36:25
 0:13:33
0:13:33