filmov
tv
DC Motor, How it works?

Показать описание
The working of a DC motor is well explained in this video with the help of animation. Construction details of DC Motor, Shunt & Series motor, concept of back EMF are also explained in this video.
DC Motor, How it works?
How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor)
How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor)
Working Principle of DC Motor (animation of elementary model)
How does an Electric Motor work? DC Motor explained
GCSE Physics - How the Electric Motor Works #80
How Motors Work For Beginners (Episode 1): The DC Motor: 032
Brushless DC Motor, How it works ?
Amazing Motor // Power Of Motor free 500 volt // @Technicalsourav507
How DC Motors Work
Super Simple DC Motor
How DC motors and universal motors work
AC Motor Vs DC Motor | Key Difference between DC and AC Motors
DC Motor - 3 Coil, How it works ?
Working principle of dc motor with animation | How does electric-dc motor works? | Mruduraj
How does an Electric Motor Work? The fundamental concept of Motor | electric Motor
How DC motors work - Electromagnetic Field and 3D animation
Electric Motor
Brushless Motor - How they work BLDC ESC PWM
How Electric Motor Work - 3D Animation
How a Brushless DC Motor Works
Working Principle of DC Generator | [Electric Machine #1]
Brushless DC motor animation
Class 10 - Physics - Chapter 15 - Lecture 4 - 15.4 D.C. Motor - Allied Schools
Комментарии
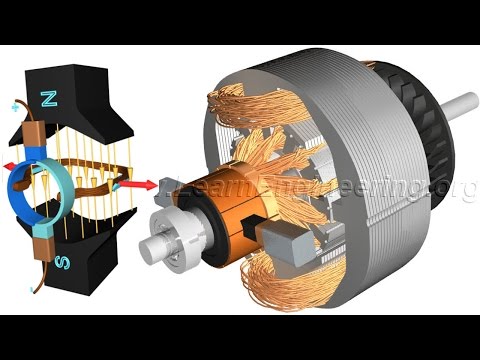 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:15:32
0:15:32
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:13:45
0:13:45
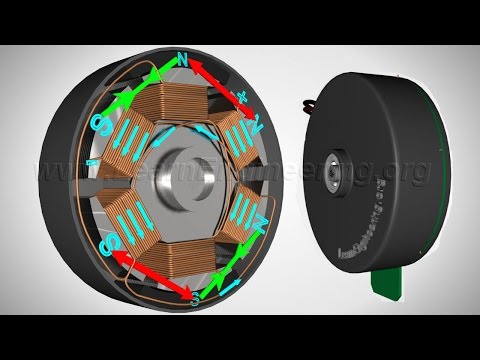 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:02:13
0:02:13
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:04:32
0:04:32
 0:10:35
0:10:35
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:16:12
0:16:12
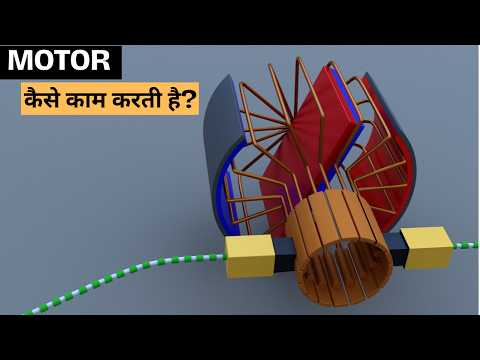 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:11:44
0:11:44