filmov
tv
Gravitational Fields | A-Level Physics | Doodle Science
Показать описание
A Level Physics
Doodle Science teaches you high school and College physics in a less boring way in almost no time!
Script:
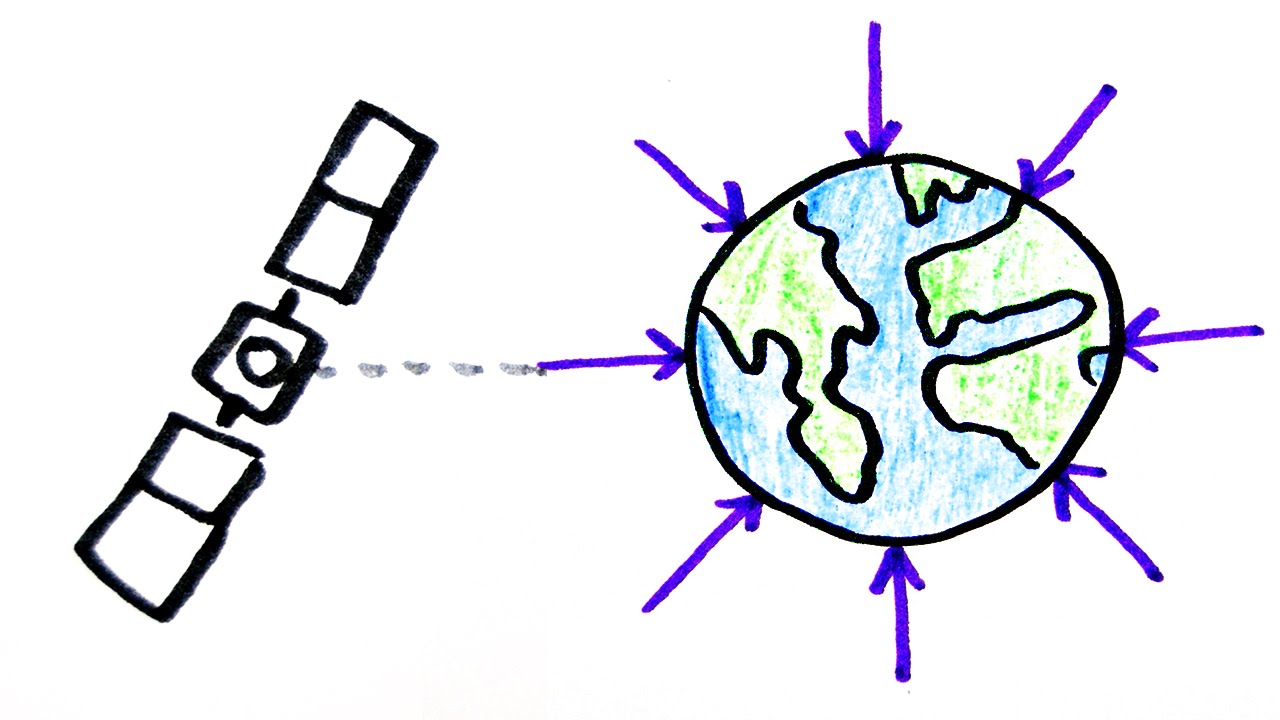
A gravitational field is a region around one mass, which affects other nearby masses. It is very weak however which is why the effect is only significant on large objects like the Earth. We can represent the Earth’s gravitational field by drawing field lines showing the direction of the gravitational force on masses in the field. In this case the field is radial and equally spread around the earth. On the surface of the earth the gravitational field is approximately uniform because the field lines are virtually pointing in the same direction and are equally spaced. This is why we assume the acceleration due to gravity is a constant of 9.81m/s^2 because the change at small vertical heights is negligible.
Newton’s law of gravitation states that all masses attract each other with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two centres of mass. This gives us the equation F= - GMm/r^2. Where G is the universal gravitational constant of 6.67x10^-11; M is the mass of the larger body; m is the mass of the smaller body; and r is the distance between the centres of mass of the two bodies. The minus sign simply refers to the to the fact that the force is attractive. For example, two bodies, one of mass 6kg and the other of mass 20kg are placed 50cm apart. From this we can work out the gravitational force acting on each object as 3.20x10^-8N. The force acting on each body is equal because they are attracted to each other.
The gravitational field strength is the force per unit mass at a point in a gravitational field. For a uniform field the equation is F/m, where F is the force experienced by the body and m is the mass of the body. For a radial field, the gravitational field strength obeys an inverse square law. The equation for it is g=GM/r^2. You can see how the gravitational field strength would decrease the further you were from the centre of the body producing the field.
This formula can be used to work out the masses of celestial bodies. For example, given that the gravitational field strength on the earth’s surface is 9.81 N/kg and the radius of the earth is 6400km, we can work out the mass of the earth to be 6.02x10^24kg.
When considering planetary motion, the gravitational force acting on the body orbiting is equal to the centripetal force because the force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion. By equating the two formulas and using the formula for the speed of an object in circular motion we get the equation T^2=(4π^2/GM)r^3. Where T is the orbital period in seconds and r is the distance between the centres of mass of the orbiting body and body being orbited. This equation shows Kepler’s third law which states that the T^2 is directly proportional to r^3. This also suggests that for a set of celestial bodies (e.g. the planets of our solar system) orbiting the same large body (e.g. the sun), T^2/r^3 is a constant and is equal for all the celestial bodies.
For example, given that it takes 365 days for the Earth to orbit the sun and that the distance of the earth from the centre of the sun is 1.5x10^11m. We can work out the mass of the sun to be about 2.00x10^30kg.
Given that the orbital period of mars is 687 days, we can use the Earth’s orbital characteristics to work how far Mars is from the centre of the Sun as being 2.29x10^11m.
A geostationary orbit is an orbit around the Earth whose orbital period is 24 hours. They are located above the equator and are always vertically above the same point on the surface of the Earth. This makes them useful for TV satellites because the dishes can be pointed to a fixed point in the sky. Which is quite convenient I’d say.
References:
1. CGP AS & A2 Physics for OCR A, ISBN: 9781847624192
Doodle Science teaches you high school and College physics in a less boring way in almost no time!
Script:
A gravitational field is a region around one mass, which affects other nearby masses. It is very weak however which is why the effect is only significant on large objects like the Earth. We can represent the Earth’s gravitational field by drawing field lines showing the direction of the gravitational force on masses in the field. In this case the field is radial and equally spread around the earth. On the surface of the earth the gravitational field is approximately uniform because the field lines are virtually pointing in the same direction and are equally spaced. This is why we assume the acceleration due to gravity is a constant of 9.81m/s^2 because the change at small vertical heights is negligible.
Newton’s law of gravitation states that all masses attract each other with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two centres of mass. This gives us the equation F= - GMm/r^2. Where G is the universal gravitational constant of 6.67x10^-11; M is the mass of the larger body; m is the mass of the smaller body; and r is the distance between the centres of mass of the two bodies. The minus sign simply refers to the to the fact that the force is attractive. For example, two bodies, one of mass 6kg and the other of mass 20kg are placed 50cm apart. From this we can work out the gravitational force acting on each object as 3.20x10^-8N. The force acting on each body is equal because they are attracted to each other.
The gravitational field strength is the force per unit mass at a point in a gravitational field. For a uniform field the equation is F/m, where F is the force experienced by the body and m is the mass of the body. For a radial field, the gravitational field strength obeys an inverse square law. The equation for it is g=GM/r^2. You can see how the gravitational field strength would decrease the further you were from the centre of the body producing the field.
This formula can be used to work out the masses of celestial bodies. For example, given that the gravitational field strength on the earth’s surface is 9.81 N/kg and the radius of the earth is 6400km, we can work out the mass of the earth to be 6.02x10^24kg.
When considering planetary motion, the gravitational force acting on the body orbiting is equal to the centripetal force because the force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion. By equating the two formulas and using the formula for the speed of an object in circular motion we get the equation T^2=(4π^2/GM)r^3. Where T is the orbital period in seconds and r is the distance between the centres of mass of the orbiting body and body being orbited. This equation shows Kepler’s third law which states that the T^2 is directly proportional to r^3. This also suggests that for a set of celestial bodies (e.g. the planets of our solar system) orbiting the same large body (e.g. the sun), T^2/r^3 is a constant and is equal for all the celestial bodies.
For example, given that it takes 365 days for the Earth to orbit the sun and that the distance of the earth from the centre of the sun is 1.5x10^11m. We can work out the mass of the sun to be about 2.00x10^30kg.
Given that the orbital period of mars is 687 days, we can use the Earth’s orbital characteristics to work how far Mars is from the centre of the Sun as being 2.29x10^11m.
A geostationary orbit is an orbit around the Earth whose orbital period is 24 hours. They are located above the equator and are always vertically above the same point on the surface of the Earth. This makes them useful for TV satellites because the dishes can be pointed to a fixed point in the sky. Which is quite convenient I’d say.
References:
1. CGP AS & A2 Physics for OCR A, ISBN: 9781847624192
Комментарии
 0:22:35
0:22:35
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:12:48
0:12:48
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:50:13
0:50:13
 0:41:06
0:41:06
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:12:11
0:12:11
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:22:42
0:22:42
 0:20:21
0:20:21
 0:40:50
0:40:50
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:21:28
0:21:28
 0:16:54
0:16:54
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:12:30
0:12:30