filmov
tv
Supernova 1987A

Показать описание
Thanks for watching!
Subscribe for new videos
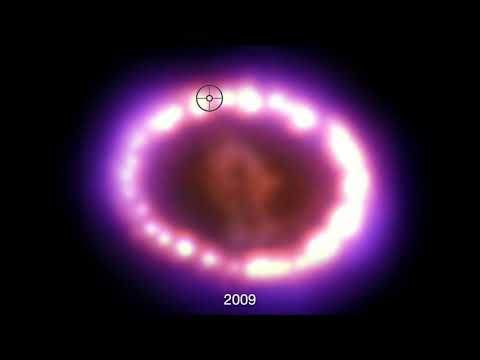
Supernova 1987A is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, 165,000 light-years from Earth.
Supernova 1987A was a unique event that originated relatively close, about 168,000 light-years away, in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. The outburst was of such power that it is estimated to have spewed energy equivalent to 100 million suns, which is why it was possible to see it in our night sky.
Due to this brutal amount of energy, the brightness in the sky remained for several months. Once it disappeared from our view, the remnant of the explosion became a cloud of dust and gas that astronomers have continued to study ever since.
Scientists searched within this cloud for a neutron star, as theory suggested that a supernova with such a large amount of mass and energy should have collapsed to give life to this small, dense, energy-filled object, which should have been difficult to miss.
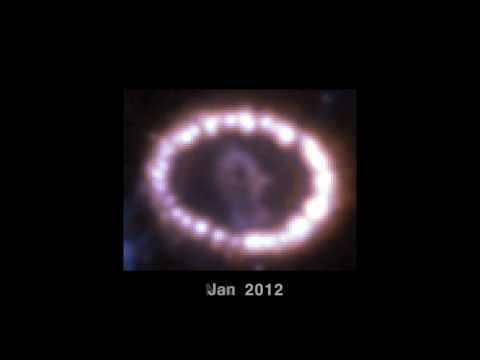
However, for 32 years such a neutron star was nowhere to be seen. Some astronomers were convinced that it had to be submerged within the dust cloud, while others suggested that it might possibly have collapsed into a black hole. But the more pessimistic ones began to question the theories we have about supernovae, which could be completely wrong, and the reality is that there was nothing left at all after the explosion.
More than 32 years later, we finally have an answer. Researchers at Cardiff University, as part of a new study, claim to have found the neutron star that was born from Supernova 1987A.
According to the data, the neutron star was hidden in the dense dust cloud, and they used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, an observatory that is capable of analyzing submillimeter wavelengths. With this, they set about the task of examining the supernova remnant and found that some of the dust appeared brighter than the rest.
Mikako Matsuura, head of the study, mentioned:
"Although the light from the neutron star is absorbed by the surrounding dust cloud, this in turn causes the cloud to glow in submillimeter light, which is now possible to observe using the extremely sensitive ALMA telescope."
This finding not only provides new data for studying supernovae, but also helps to provide some reassurance that the current theories out there about supernovae are accurate. Astronomers predict that the dust cloud could begin to disperse in the future, making the neutron star directly visible.
#Shorts #TikTok #Universe
Subscribe for new videos
Supernova 1987A is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, 165,000 light-years from Earth.
Supernova 1987A was a unique event that originated relatively close, about 168,000 light-years away, in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. The outburst was of such power that it is estimated to have spewed energy equivalent to 100 million suns, which is why it was possible to see it in our night sky.
Due to this brutal amount of energy, the brightness in the sky remained for several months. Once it disappeared from our view, the remnant of the explosion became a cloud of dust and gas that astronomers have continued to study ever since.
Scientists searched within this cloud for a neutron star, as theory suggested that a supernova with such a large amount of mass and energy should have collapsed to give life to this small, dense, energy-filled object, which should have been difficult to miss.
However, for 32 years such a neutron star was nowhere to be seen. Some astronomers were convinced that it had to be submerged within the dust cloud, while others suggested that it might possibly have collapsed into a black hole. But the more pessimistic ones began to question the theories we have about supernovae, which could be completely wrong, and the reality is that there was nothing left at all after the explosion.
More than 32 years later, we finally have an answer. Researchers at Cardiff University, as part of a new study, claim to have found the neutron star that was born from Supernova 1987A.
According to the data, the neutron star was hidden in the dense dust cloud, and they used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, an observatory that is capable of analyzing submillimeter wavelengths. With this, they set about the task of examining the supernova remnant and found that some of the dust appeared brighter than the rest.
Mikako Matsuura, head of the study, mentioned:
"Although the light from the neutron star is absorbed by the surrounding dust cloud, this in turn causes the cloud to glow in submillimeter light, which is now possible to observe using the extremely sensitive ALMA telescope."
This finding not only provides new data for studying supernovae, but also helps to provide some reassurance that the current theories out there about supernovae are accurate. Astronomers predict that the dust cloud could begin to disperse in the future, making the neutron star directly visible.
#Shorts #TikTok #Universe
Комментарии
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:29:06
0:29:06
 0:12:13
0:12:13
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:02:24
0:02:24