filmov
tv
Properties Of Fluids | Viscosity | Properties |Fluid Mechanics | Hydraulic Machines | Telugu lecture

Показать описание
Properties Of Fluids | Viscosity | Properties |Fluid Mechanics | Hydraulic Machines | Telugu lecture
Hi This is Upendra Kumar Malla. Welcome to my channel .I want to provide some basic information about Mechanical engineering and Industrial safety .
Telegram group link 👇👇
App link -Google play store link
For Desktop / Web access -
Org code: arfxv
Fluids are a fundamental category of matter that includes liquids and gases. They possess various properties that define their behavior and interactions. Here are some key properties of fluids:
Density: Density is the mass per unit volume of a fluid. It determines how heavy a given volume of fluid is. Liquids and gases have different densities, with gases typically being much less dense than liquids.
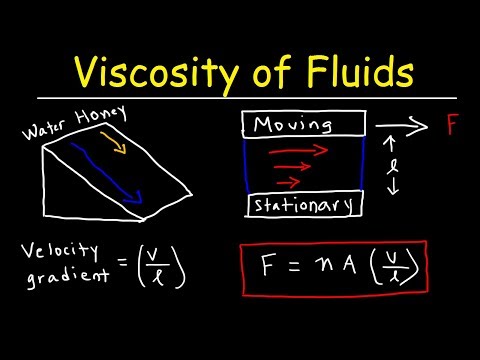
Viscosity: Viscosity measures a fluid's resistance to flow. High-viscosity fluids are thick and resist flowing easily, while low-viscosity fluids are more fluidic. Honey, for example, has high viscosity, while water has relatively low viscosity.
Pressure: Pressure is the force exerted per unit area by a fluid. It's the property that gives rise to fluid flow. Pressure is crucial for understanding fluid dynamics, aerodynamics, and hydrodynamics.
Buoyancy: Buoyancy is the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid. It's responsible for the phenomenon of objects floating or sinking in fluids and is a result of the fluid pressure difference between the top and bottom of the submerged object.
Compressibility: This property refers to how much a fluid's volume can change when subjected to pressure changes. Gases are more compressible than liquids. The compressibility of a fluid affects its response to changes in pressure and temperature.
Surface Tension: Surface tension is the property of liquids that causes them to behave like they have a "skin" on their surface. It's responsible for phenomena like capillary action and the formation of droplets.
Temperature and Thermal Expansion: Fluids expand or contract with changes in temperature. This is described by the coefficient of thermal expansion, which quantifies the fractional change in volume per degree change in temperature.
Elasticity and Bulk Modulus: Elasticity measures a fluid's ability to return to its original shape after deformation. Bulk modulus is a measure of a fluid's resistance to changes in volume when subjected to external pressure.
Fluid Dynamics: Fluid dynamics is the study of fluid behavior in motion. It involves concepts like flow velocity, turbulence, laminar flow (smooth flow), and turbulent flow (chaotic flow).
Hydrostatic Pressure: Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest due to the weight of the fluid above it. It increases with depth in a fluid.
Reynolds Number: In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the flow of a fluid. It helps determine whether flow is laminar or turbulent.
These properties play a significant role in various scientific, engineering, and everyday situations, from understanding weather patterns and designing aircraft to analyzing blood flow in the human body and predicting ocean currents. Fluid mechanics is a branch of physics and engineering that extensively studies these properties and their effects on fluid behavior.
#manometer #utubemanometer #fluidmechanics #hydraulics #invertermanometer #mechanicalengineering #compitativeexams #turbines #typesofmanometers #fluidmechanicsandhydraulicmachines #nozzles #turbineclassification #powerplant
Hi This is Upendra Kumar Malla. Welcome to my channel .I want to provide some basic information about Mechanical engineering and Industrial safety .
Telegram group link 👇👇
App link -Google play store link
For Desktop / Web access -
Org code: arfxv
Fluids are a fundamental category of matter that includes liquids and gases. They possess various properties that define their behavior and interactions. Here are some key properties of fluids:
Density: Density is the mass per unit volume of a fluid. It determines how heavy a given volume of fluid is. Liquids and gases have different densities, with gases typically being much less dense than liquids.
Viscosity: Viscosity measures a fluid's resistance to flow. High-viscosity fluids are thick and resist flowing easily, while low-viscosity fluids are more fluidic. Honey, for example, has high viscosity, while water has relatively low viscosity.
Pressure: Pressure is the force exerted per unit area by a fluid. It's the property that gives rise to fluid flow. Pressure is crucial for understanding fluid dynamics, aerodynamics, and hydrodynamics.
Buoyancy: Buoyancy is the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid. It's responsible for the phenomenon of objects floating or sinking in fluids and is a result of the fluid pressure difference between the top and bottom of the submerged object.
Compressibility: This property refers to how much a fluid's volume can change when subjected to pressure changes. Gases are more compressible than liquids. The compressibility of a fluid affects its response to changes in pressure and temperature.
Surface Tension: Surface tension is the property of liquids that causes them to behave like they have a "skin" on their surface. It's responsible for phenomena like capillary action and the formation of droplets.
Temperature and Thermal Expansion: Fluids expand or contract with changes in temperature. This is described by the coefficient of thermal expansion, which quantifies the fractional change in volume per degree change in temperature.
Elasticity and Bulk Modulus: Elasticity measures a fluid's ability to return to its original shape after deformation. Bulk modulus is a measure of a fluid's resistance to changes in volume when subjected to external pressure.
Fluid Dynamics: Fluid dynamics is the study of fluid behavior in motion. It involves concepts like flow velocity, turbulence, laminar flow (smooth flow), and turbulent flow (chaotic flow).
Hydrostatic Pressure: Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest due to the weight of the fluid above it. It increases with depth in a fluid.
Reynolds Number: In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the flow of a fluid. It helps determine whether flow is laminar or turbulent.
These properties play a significant role in various scientific, engineering, and everyday situations, from understanding weather patterns and designing aircraft to analyzing blood flow in the human body and predicting ocean currents. Fluid mechanics is a branch of physics and engineering that extensively studies these properties and their effects on fluid behavior.
#manometer #utubemanometer #fluidmechanics #hydraulics #invertermanometer #mechanicalengineering #compitativeexams #turbines #typesofmanometers #fluidmechanicsandhydraulicmachines #nozzles #turbineclassification #powerplant
Комментарии
 0:12:55
0:12:55
 0:10:53
0:10:53
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:10:59
0:10:59
 0:55:33
0:55:33
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:15:30
0:15:30
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:36:24
0:36:24
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:07:07
0:07:07
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:08:32
0:08:32