filmov
tv
What is Biomass Power?

Показать описание
Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals, containing stored chemical energy from the sun
Biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to renewable liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes.
Converting biomass to energy
Biomass is converted to energy through various processes, including:
• Direct combustion (burning) to produce heat
• Thermochemical conversion to produce solid, gaseous, and liquid fuels
• Chemical conversion to produce liquid fuels
• Biological conversion to produce liquid and gaseous fuels
Direct combustion is the most common method for converting biomass to useful energy. All biomass can be burned directly for heating buildings and water, for industrial process heat, and for generating electricity in steam turbines.
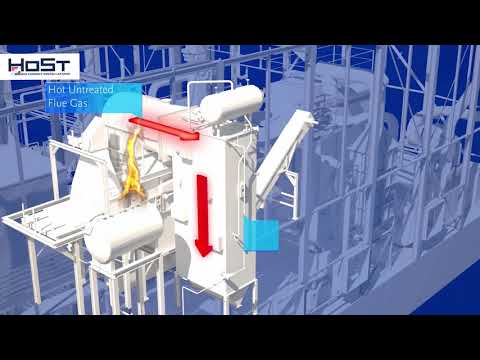
Thermochemical conversion of biomass includes pyrolysis and gasification.
Both are thermal decomposition processes in which biomass feedstock materials are heated in closed, pressurized vessels called gassifiers at high temperatures.
• Pyrolysis entails heating organic materials to 800–900oF (400–500 oC) in the near complete absence of free oxygen.
• Biomass pyrolysis produces fuels such as charcoal, bio-oil, renewable diesel, methane, and hydrogen.
• Hydrotreating is used to process bio-oil (produced by fast pyrolysis) with hydrogen under elevated temperatures and pressures in the presence of a catalyst
• Produce renewable diesel, renewable gasoline, and renewable jet fuel.
• Gasification entails heating organic materials to 800–900oC with oxygen and/or steam into the vessel
• Produce a carbon monoxide and syngas which can be used as a fuel for diesel engines, for heating, and for generating electricity in gas turbines.
A chemical conversion process is used for converting vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases into fatty acid methyl esters, which are used to produce biodiesel.
Biological conversion includes fermentation producing ethanol and anaerobic digestion producing renewable natural gas.
Advantages
Reliable Source
Is always and widely available as a renewable source of energy - the organic materials used to produce biomass are infinite, since our society consistently produces waste such as garbage, wood, and manure.
Carbon Neutral
Only release the same amount of carbon into the atmosphere as was absorbed by plants in the course of their life cycle
Garbage in Landfills
By burning solid waste, the amount of garbage dumped in landfills is reduced by 60 to 90 percent and reduces the cost of landfill disposal and amount of land required.
Expense
Manufacturers and producers are able to generate higher profits from a lower output.
Disadvantages
Efficiency
It is not as efficient as fossil fuels, has to be fortified with fossil fuels to increase its efficiency
Clean Energy
It is not entirely clean - while biomass is carbon neutral, the use of animal and human waste escalates the amount of methane gases, which are also damaging to the environment.
Deforestation
Can lead to deforestation vast amounts of wood and other waste products have to be burned to produce the desired amount of power. While currently there is enough wood waste already, there is a risk of deforestation in the future.
Quote
“With careful management, our nature reserves could be a source of sustainable biomass”
Biomass explained - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
#climatechange #renewableenergy #climateaction #climateactionintoeducation #climateemergency #climatemponews #renewableresources #renewablefuels
Biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to renewable liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes.
Converting biomass to energy
Biomass is converted to energy through various processes, including:
• Direct combustion (burning) to produce heat
• Thermochemical conversion to produce solid, gaseous, and liquid fuels
• Chemical conversion to produce liquid fuels
• Biological conversion to produce liquid and gaseous fuels
Direct combustion is the most common method for converting biomass to useful energy. All biomass can be burned directly for heating buildings and water, for industrial process heat, and for generating electricity in steam turbines.
Thermochemical conversion of biomass includes pyrolysis and gasification.
Both are thermal decomposition processes in which biomass feedstock materials are heated in closed, pressurized vessels called gassifiers at high temperatures.
• Pyrolysis entails heating organic materials to 800–900oF (400–500 oC) in the near complete absence of free oxygen.
• Biomass pyrolysis produces fuels such as charcoal, bio-oil, renewable diesel, methane, and hydrogen.
• Hydrotreating is used to process bio-oil (produced by fast pyrolysis) with hydrogen under elevated temperatures and pressures in the presence of a catalyst
• Produce renewable diesel, renewable gasoline, and renewable jet fuel.
• Gasification entails heating organic materials to 800–900oC with oxygen and/or steam into the vessel
• Produce a carbon monoxide and syngas which can be used as a fuel for diesel engines, for heating, and for generating electricity in gas turbines.
A chemical conversion process is used for converting vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases into fatty acid methyl esters, which are used to produce biodiesel.
Biological conversion includes fermentation producing ethanol and anaerobic digestion producing renewable natural gas.
Advantages
Reliable Source
Is always and widely available as a renewable source of energy - the organic materials used to produce biomass are infinite, since our society consistently produces waste such as garbage, wood, and manure.
Carbon Neutral
Only release the same amount of carbon into the atmosphere as was absorbed by plants in the course of their life cycle
Garbage in Landfills
By burning solid waste, the amount of garbage dumped in landfills is reduced by 60 to 90 percent and reduces the cost of landfill disposal and amount of land required.
Expense
Manufacturers and producers are able to generate higher profits from a lower output.
Disadvantages
Efficiency
It is not as efficient as fossil fuels, has to be fortified with fossil fuels to increase its efficiency
Clean Energy
It is not entirely clean - while biomass is carbon neutral, the use of animal and human waste escalates the amount of methane gases, which are also damaging to the environment.
Deforestation
Can lead to deforestation vast amounts of wood and other waste products have to be burned to produce the desired amount of power. While currently there is enough wood waste already, there is a risk of deforestation in the future.
Quote
“With careful management, our nature reserves could be a source of sustainable biomass”
Biomass explained - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
#climatechange #renewableenergy #climateaction #climateactionintoeducation #climateemergency #climatemponews #renewableresources #renewablefuels
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:45:08
0:45:08
 0:03:22
0:03:22
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:04:47
0:04:47