filmov
tv
cryptography, cryptography introduction, cryptography definition, cryptography example

Показать описание
Cryptography is a complex and fascinating field of study and practice that revolves around the art and science of securing sensitive information through the use of mathematical techniques and algorithms. It plays a pivotal role in modern digital society, offering protection for data in transit and data at rest, as well as enabling secure communication and authentication in various applications. Here's a more detailed description of cryptography:
**Cryptography Defined:**
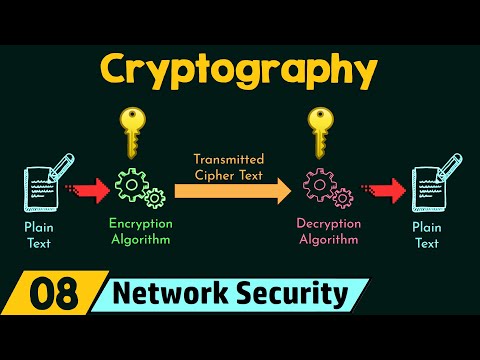
Cryptography is the discipline that deals with transforming plain, understandable data (plaintext) into an unintelligible form (ciphertext) using mathematical algorithms and encryption keys. It is designed to ensure that only authorized individuals or systems can decipher and access the original information. Cryptography encompasses a wide range of techniques and practices aimed at achieving the following key objectives:
**1. Confidentiality:** Cryptography ensures that sensitive information remains confidential, meaning that only authorized parties can understand the content of the data. It protects against eavesdropping and unauthorized access to confidential data.
**2. Integrity:** Cryptographic techniques are used to verify that data has not been tampered with during transmission or storage. Any unauthorized changes to the data can be detected through cryptographic integrity checks.
**3. Authentication:** Cryptography plays a crucial role in verifying the identity of individuals, devices, or systems. It helps establish trust by confirming the legitimacy of entities involved in communication or data exchange.
**4. Non-repudiation:** Non-repudiation ensures that an entity cannot deny the authenticity of a message or action. Digital signatures, a cryptographic technique, are often used to achieve non-repudiation.
**Key Elements of Cryptography:**
Cryptography relies on several key elements and concepts:
**1. Encryption Algorithms:** Encryption algorithms are mathematical procedures used to transform plaintext into ciphertext and vice versa. Different algorithms offer varying levels of security and efficiency.
**2. Cryptographic Keys:** Keys are essential components of cryptography. In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption. In asymmetric encryption, a pair of keys (public and private) is used for secure communication and authentication.
**3. Hash Functions:** Hash functions convert data into fixed-length strings of characters (hash values). They are used for data integrity checks and creating digital signatures.
**4. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):** PKI is a framework that manages digital certificates and keys to facilitate secure communication over the internet. Certificate authorities (CAs) play a crucial role in issuing digital certificates.
**5. Digital Signatures:** Digital signatures are cryptographic techniques that verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents. They are generated using the sender's private key and can be verified using the sender's public key.
**Applications of Cryptography:**
Cryptography finds applications in various domains, including:
- **Secure Communication:** Encrypting emails, messages, and internet traffic to protect against eavesdropping and data breaches.
- **Online Banking and E-commerce:** Securing financial transactions and customer data during online purchases.
- **Data Storage:** Encrypting sensitive files and data on storage devices to prevent unauthorized access.
- **Authentication:** Verifying user identities through password hashing and multi-factor authentication.
- **Blockchain Technology:** Enabling secure, decentralized transactions and record-keeping through cryptographic techniques.
- **Military and National Security:** Protecting classified information and communications from adversaries.
- **Healthcare:** Safeguarding patient data and medical records to ensure privacy and compliance with regulations.
In an era where digital information is increasingly valuable and vulnerable, cryptography serves as a cornerstone of cybersecurity, providing the means to protect sensitive data and maintain the trust of individuals, businesses, and governments in the digital age. It continues to evolve in response to emerging threats and technologies, making it an ongoing and dynamic field of study and practice.
**Cryptography Defined:**
Cryptography is the discipline that deals with transforming plain, understandable data (plaintext) into an unintelligible form (ciphertext) using mathematical algorithms and encryption keys. It is designed to ensure that only authorized individuals or systems can decipher and access the original information. Cryptography encompasses a wide range of techniques and practices aimed at achieving the following key objectives:
**1. Confidentiality:** Cryptography ensures that sensitive information remains confidential, meaning that only authorized parties can understand the content of the data. It protects against eavesdropping and unauthorized access to confidential data.
**2. Integrity:** Cryptographic techniques are used to verify that data has not been tampered with during transmission or storage. Any unauthorized changes to the data can be detected through cryptographic integrity checks.
**3. Authentication:** Cryptography plays a crucial role in verifying the identity of individuals, devices, or systems. It helps establish trust by confirming the legitimacy of entities involved in communication or data exchange.
**4. Non-repudiation:** Non-repudiation ensures that an entity cannot deny the authenticity of a message or action. Digital signatures, a cryptographic technique, are often used to achieve non-repudiation.
**Key Elements of Cryptography:**
Cryptography relies on several key elements and concepts:
**1. Encryption Algorithms:** Encryption algorithms are mathematical procedures used to transform plaintext into ciphertext and vice versa. Different algorithms offer varying levels of security and efficiency.
**2. Cryptographic Keys:** Keys are essential components of cryptography. In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption. In asymmetric encryption, a pair of keys (public and private) is used for secure communication and authentication.
**3. Hash Functions:** Hash functions convert data into fixed-length strings of characters (hash values). They are used for data integrity checks and creating digital signatures.
**4. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):** PKI is a framework that manages digital certificates and keys to facilitate secure communication over the internet. Certificate authorities (CAs) play a crucial role in issuing digital certificates.
**5. Digital Signatures:** Digital signatures are cryptographic techniques that verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents. They are generated using the sender's private key and can be verified using the sender's public key.
**Applications of Cryptography:**
Cryptography finds applications in various domains, including:
- **Secure Communication:** Encrypting emails, messages, and internet traffic to protect against eavesdropping and data breaches.
- **Online Banking and E-commerce:** Securing financial transactions and customer data during online purchases.
- **Data Storage:** Encrypting sensitive files and data on storage devices to prevent unauthorized access.
- **Authentication:** Verifying user identities through password hashing and multi-factor authentication.
- **Blockchain Technology:** Enabling secure, decentralized transactions and record-keeping through cryptographic techniques.
- **Military and National Security:** Protecting classified information and communications from adversaries.
- **Healthcare:** Safeguarding patient data and medical records to ensure privacy and compliance with regulations.
In an era where digital information is increasingly valuable and vulnerable, cryptography serves as a cornerstone of cybersecurity, providing the means to protect sensitive data and maintain the trust of individuals, businesses, and governments in the digital age. It continues to evolve in response to emerging threats and technologies, making it an ongoing and dynamic field of study and practice.
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:20:31
0:20:31
 0:17:56
0:17:56
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:11:55
0:11:55
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:57:40
0:57:40
 0:13:34
0:13:34
 0:20:41
0:20:41
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:12:49
0:12:49
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:18:16
0:18:16
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:00:21
0:00:21