filmov
tv
Pathway of Pain and Temperature Sensation, Dr Adel Bondok

Показать описание
Dr Adel Bondok Neuroanatomy Teaching Videos.
You should know:
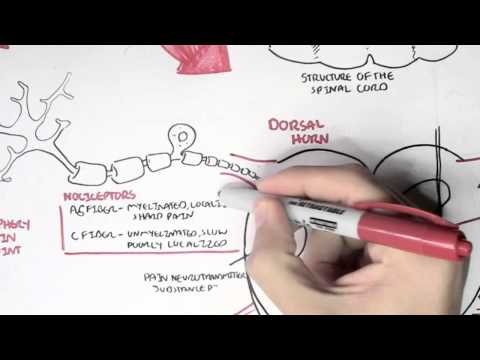
1. The receptors.
2. The pain fibers (A-delta and C-fibers).
3. The tract: lateral spinothalamic tract.
4. The 1st, 2nd and 3rd order neuron.
5. Effect of a lesion in the lateral spinothalamic tract.
Function of the Substantia Gelatinosa (lamina II):
Substantia gelatinosa consists of small neurons (Golgi type II) which have short axons. The short axons synapse with neurons of the nucleus proprius and the posteromarginal nucleus to inhibit pain transmission.
It does not contain large cells. Therefore, it does not form the lateral spinothalamic tract.
Inhibition of Pain Sensation:
1. Substantia gelatinosa cells release enkephalins which inhibit the release of substance P from the pain fibers (A-delta and C-fibers) of DRG.
2. SG cells receive excitatory impulses from the following sources for pain suppression:
a. Sensory area of the cerebral cortex via the corticospinal tract (NE).
b. Touch fibers from gracile and cuneate tracts (glutamate).
c. Raphe magnus nucleus (reticular formation) via the raphe-spinal tract (serotonin).
You should know:
1. The receptors.
2. The pain fibers (A-delta and C-fibers).
3. The tract: lateral spinothalamic tract.
4. The 1st, 2nd and 3rd order neuron.
5. Effect of a lesion in the lateral spinothalamic tract.
Function of the Substantia Gelatinosa (lamina II):
Substantia gelatinosa consists of small neurons (Golgi type II) which have short axons. The short axons synapse with neurons of the nucleus proprius and the posteromarginal nucleus to inhibit pain transmission.
It does not contain large cells. Therefore, it does not form the lateral spinothalamic tract.
Inhibition of Pain Sensation:
1. Substantia gelatinosa cells release enkephalins which inhibit the release of substance P from the pain fibers (A-delta and C-fibers) of DRG.
2. SG cells receive excitatory impulses from the following sources for pain suppression:
a. Sensory area of the cerebral cortex via the corticospinal tract (NE).
b. Touch fibers from gracile and cuneate tracts (glutamate).
c. Raphe magnus nucleus (reticular formation) via the raphe-spinal tract (serotonin).
Sensory Pathways | Touch/Proprioception vs Pain/Temperature
Sensory Pathways | Touch vs. Pain and Temperature
PAIN! Physiology - The Ascending Pathway, Descending Pain Pathway and the Substantia Gelatinosa
Pathway of Pain and Temperature Sensation, Dr Adel Bondok
Pain vs Nociception | In 2 minutes!!
Ascending Tracts | Spinothalamic Tract
Long sensory pathways
Touch, temperature, and pain
Enhanced Recovery After Anesthesia
Ascending Tracts | Pain Modulation: Gate Control Theory
The Spinothalamic Pathway EXPLAINED! | Pain & Temperature
Pain and temperature | Integumentary system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Nociceptors - An Introduction to Pain
Spinothalamic Tract | Ascending Tracts | Spinocerebellar Tract | Neuroanatomy
Somatosensory tracts | Organ Systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
Pain pathway | Pain physiology | Pain suppression system | Gate control theory | Neurophysiology
How does your brain respond to pain? - Karen D. Davis
Spinothalamic Tract and Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus Pathway | Ascending Tracts of the Spinal Cord
David Julius 'Natural products as probes of the pain pathway: from physiology to atomic structu...
Sensory Tracts - Dorsal Column (Medial lemniscus) Pathway
PAIN PATHWAYS - 1 | Paleospinothalamic Pathway | CNS | Physiology
Pathway for Temperature Sensation
Anatomy of CNS Module in Arabic 2024 (Pathway of pain and temperature below the head), Dr. Wahdan.
Neuroanatomy 12 ( Introduction 12 , pathway of pain & temperature ), dr.Wahdan
Комментарии
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:13:07
0:13:07
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:45:36
0:45:36
 0:24:12
0:24:12
 0:25:21
0:25:21
 2:18:35
2:18:35
 0:24:13
0:24:13
 0:10:45
0:10:45
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:12:17
0:12:17
 3:14:02
3:14:02
 0:07:07
0:07:07
 0:25:01
0:25:01
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:32:22
0:32:22
 0:08:50
0:08:50
 0:11:41
0:11:41
 0:14:15
0:14:15
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:07:04
0:07:04