filmov
tv
Solution of the Navier-Stokes: Hagen-Poiseuille Flow

Показать описание
MEC516/BME516 Fluid Mechanics, Chapter 4 Differential Relations for Fluid Flow, Part 6: Exact solution of the Navier-Stokes and Continuity equations for fully developed laminar flow in a round pipe (Hagen-Poiseuille Flow). The video ends with a numerical example.
Course Textbook: F.M. White and H. Xue, Fluid Mechanics, 9th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2021.
#fluidmechanics #fluiddynamics
Course Textbook: F.M. White and H. Xue, Fluid Mechanics, 9th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2021.
#fluidmechanics #fluiddynamics
Solution of the Navier-Stokes: Hagen-Poiseuille Flow
Hagen-Poiseuille flow: a detailed complete solution to the Navier-Stokes equation
Solutions to Navier-Stokes: Poiseuille and Couette Flow
Deriving Poiseuille's Law from the Navier-Stokes Equations
From Navier Stokes to Hagen Poiseuille 2
The million dollar equation (Navier-Stokes equations)
Fundamentals of Navier - Stokes Equation// Hagen- Poiseuille Flow // 1-D Viscous flow through Pipes
Navier-Stokes Equation Final Exam Question
Hagen Poiseuille Flow - Fluid Dynamics - Fluid Mechanics 1
Fluid Mechanics Lesson 11C: Navier-Stokes Solutions, Cylindrical Coordinates
Fluid Mechanics 12.5 - Hagen - Poiseuille Flow, Viscous flow in Circular Pipes
Solutions of Navier-Stokes Equations: Lecture-12B
Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation | Lecture-02 | Hagen Poiseuille Flow | Fluid Mechanics #bsc
Hagen-Poiseuille Flow Derivation
Navier-Stokes Final Exam Question (Liquid Film)
Fluid Mechanics Lesson 11D: More Solutions of the Navier-Stokes Equation
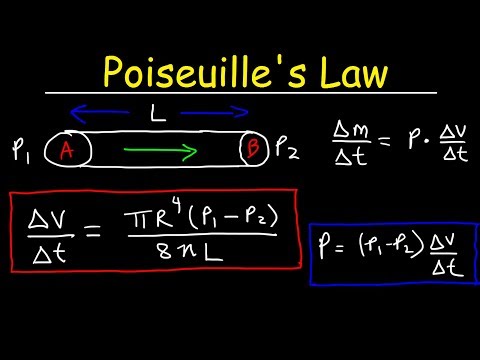
Poiseuille's Law - Pressure Difference, Volume Flow Rate, Fluid Power Physics Problems
BE112B (07) Poiseuille Flow
Fluid dynamics | Derivation of the Hagen–Poiseuille Law
Stokes To Poiseuille
[Fluid Dynamics: Equation] Derivation of the Navier-Stokes equation
Pressure Driven Pipe Flow Simulation in Python | Hagen-Poiseuille Profile
Description and Derivation of the Navier-Stokes Equations
Worst equation ever? The Navier-Stokes equation for incompressible flow (Fluid Dynamics w O Cleynen)
Комментарии
 0:21:29
0:21:29
 0:21:33
0:21:33
 0:21:13
0:21:13
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:12:22
0:12:22
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:45:54
0:45:54
 0:14:55
0:14:55
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:13:20
0:13:20
 0:27:18
0:27:18
 0:31:01
0:31:01
 0:22:25
0:22:25
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:17:21
0:17:21
 0:11:28
0:11:28
 0:17:19
0:17:19
 0:08:04
0:08:04
![[Fluid Dynamics: Equation]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/VADrf78Qu0I/hqdefault.jpg) 0:31:02
0:31:02
 0:28:16
0:28:16
 0:11:18
0:11:18
 0:20:46
0:20:46