filmov
tv
Gyri and Sulci, Cerebral Cortex, and White Matter #brain #medical

Показать описание
An average adult human brain is about the size of a medium cauliflower, measuring roughly 15 centimetres or 6 inches in length.
It typically weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kilograms.
it is surrounded and protected by cerebrospinal fluid which cushions the brain and helps to remove waste.
Here is a brief overview of all parts of the brain.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain, accounting for approximately 85% of its weight. It is responsible for most higher-order cognitive functions.
1. Hemispheres:
- Right hemispheres
- Left Hemisphere
2. Lobes of the Cerebrum
- Frontal Lobe
- Parietal Lobe
- Temporal Lobe
- Occipital Lobe
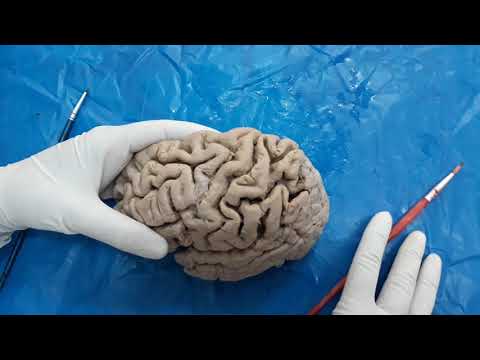
3. Gyri and Sulci:
4. Cerebral Cortex:
5. White Matter:
6. Basal Ganglia:
7. Limbic System:
Cerebellum:
The cerebellum, often referred to as the "little brain" due to its appearance and size relative to the cerebrum, is an essential structure located underneath the occipital lobes of the cerebrum at the back of the brain.
It has various parts:
1. Deep Cerebellar Nuclei
2. Peduncles
• Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
• Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
• Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
Brainstem
The brainstem is located at the base of the brain. It serves as the bridge connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord.
1. Components
• Midbrain or Mesencephalon
• Pons
• Medulla Oblongata
Thalamus
• The thalamus is located in the center of the brain, just above the brainstem, and is nestled between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. Each hemisphere of the brain contains a thalamus.
It performs various functions:
• Relay Station
• Motor Functions
• Sleep & Wakefulness
• Consciousness
• Pain Perception
Hypothalamus
• The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, approximately above the pituitary gland, and forms the lower walls and floor of the third ventricle in the brain.
• It's about the size of an almond and consists of various nuclei and nerve fibers.
Hypothalamus perform various functions,:
• Endocrine System Regulation
• Autonomic Nervous System Regulation
• Temperature Regulation
• Hunger and Thirst Regulation
• sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms
• Emotion and Behaviour
• And Memory
limbic system
Limbic system is a group of interconnected structures. Here are some of the primary components
• Amygdala
• Hippocampus
• Thalamus
• Hypothalamus
• Cingulate Gyrus
• Parahippocampal Gyrus
• Basal Ganglia
• Olfactory Bulbs
pituitary gland
• The pituitary gland is situated at the base of the brain, right below the hypothalamus, and is housed within a bony structure called the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
• It is attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk known as the infundibulum or pituitary stalk.
The gland is divided into two primary sections:
1. Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis):
• Hormones produced and released by the anterior pituitary include:
• Growth Hormone (GH)
• Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
• Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
• Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
• Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
• Prolactin (PRL)
• And, Endorphins and Enkephalins
2. Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis):
• Hormones released by the posterior pituitary include:
• Oxytocin
• Vasopressin
basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are composed of several interconnected nuclei, which includes:
• Striatum
• Globus Pallidus
• Subthalamic Nucleus (STN)
• And, Substantia Nigra
Basal ganglia perform several functions, which include:
• Motor Control
• Procedural Learning
• Emotions and Behaviour
• Cognitive Functions
corpus callosum
• The corpus callosum can be segmented into different regions based on its anterior-to-posterior orientation:
• Rostrum
• Genu
• Body (or Trunk)
• And, Splenium
corpus callosum perform several functions, which include:
• Interhemispheric Communication
• Facilitate Learning
• Redundancy and Recovery
Ventricles
The ventricles of the brain are a connected system of cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). These cavities not only serve as a reservoir for CSF but also play a role in its circulation and in cushioning the brain.
The ventricular system comprises four main ventricles:
• Lateral Ventricles, (First and Second Ventricles):
• Third Ventricle:
• Fourth Ventricle:
Functions:
• Cerebrospinal Fluid or CSF Production:
• Brain Protection:
• Nutrient and Waste Transport:
This was the basic overview of human brain, its components, and functions which brain and its components perform. We will go in more detail in some other video.
It typically weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kilograms.
it is surrounded and protected by cerebrospinal fluid which cushions the brain and helps to remove waste.
Here is a brief overview of all parts of the brain.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain, accounting for approximately 85% of its weight. It is responsible for most higher-order cognitive functions.
1. Hemispheres:
- Right hemispheres
- Left Hemisphere
2. Lobes of the Cerebrum
- Frontal Lobe
- Parietal Lobe
- Temporal Lobe
- Occipital Lobe
3. Gyri and Sulci:
4. Cerebral Cortex:
5. White Matter:
6. Basal Ganglia:
7. Limbic System:
Cerebellum:
The cerebellum, often referred to as the "little brain" due to its appearance and size relative to the cerebrum, is an essential structure located underneath the occipital lobes of the cerebrum at the back of the brain.
It has various parts:
1. Deep Cerebellar Nuclei
2. Peduncles
• Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
• Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
• Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
Brainstem
The brainstem is located at the base of the brain. It serves as the bridge connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord.
1. Components
• Midbrain or Mesencephalon
• Pons
• Medulla Oblongata
Thalamus
• The thalamus is located in the center of the brain, just above the brainstem, and is nestled between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. Each hemisphere of the brain contains a thalamus.
It performs various functions:
• Relay Station
• Motor Functions
• Sleep & Wakefulness
• Consciousness
• Pain Perception
Hypothalamus
• The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, approximately above the pituitary gland, and forms the lower walls and floor of the third ventricle in the brain.
• It's about the size of an almond and consists of various nuclei and nerve fibers.
Hypothalamus perform various functions,:
• Endocrine System Regulation
• Autonomic Nervous System Regulation
• Temperature Regulation
• Hunger and Thirst Regulation
• sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms
• Emotion and Behaviour
• And Memory
limbic system
Limbic system is a group of interconnected structures. Here are some of the primary components
• Amygdala
• Hippocampus
• Thalamus
• Hypothalamus
• Cingulate Gyrus
• Parahippocampal Gyrus
• Basal Ganglia
• Olfactory Bulbs
pituitary gland
• The pituitary gland is situated at the base of the brain, right below the hypothalamus, and is housed within a bony structure called the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
• It is attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk known as the infundibulum or pituitary stalk.
The gland is divided into two primary sections:
1. Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis):
• Hormones produced and released by the anterior pituitary include:
• Growth Hormone (GH)
• Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
• Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
• Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
• Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
• Prolactin (PRL)
• And, Endorphins and Enkephalins
2. Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis):
• Hormones released by the posterior pituitary include:
• Oxytocin
• Vasopressin
basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are composed of several interconnected nuclei, which includes:
• Striatum
• Globus Pallidus
• Subthalamic Nucleus (STN)
• And, Substantia Nigra
Basal ganglia perform several functions, which include:
• Motor Control
• Procedural Learning
• Emotions and Behaviour
• Cognitive Functions
corpus callosum
• The corpus callosum can be segmented into different regions based on its anterior-to-posterior orientation:
• Rostrum
• Genu
• Body (or Trunk)
• And, Splenium
corpus callosum perform several functions, which include:
• Interhemispheric Communication
• Facilitate Learning
• Redundancy and Recovery
Ventricles
The ventricles of the brain are a connected system of cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). These cavities not only serve as a reservoir for CSF but also play a role in its circulation and in cushioning the brain.
The ventricular system comprises four main ventricles:
• Lateral Ventricles, (First and Second Ventricles):
• Third Ventricle:
• Fourth Ventricle:
Functions:
• Cerebrospinal Fluid or CSF Production:
• Brain Protection:
• Nutrient and Waste Transport:
This was the basic overview of human brain, its components, and functions which brain and its components perform. We will go in more detail in some other video.
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:22:09
0:22:09
 0:26:34
0:26:34
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:13:22
0:13:22
 0:12:17
0:12:17
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:35:23
0:35:23
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:16:03
0:16:03
 0:19:45
0:19:45
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:17:23
0:17:23
 0:19:15
0:19:15
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:35:32
0:35:32
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:59
0:00:59