filmov
tv
What is a Transistor | Working Principles

Показать описание
=============================
▶ Check out the full blog post over at
=============================
⌚Timestamps:
00:00 - Intro
00:59 - Types of transistors
01:19 - What is a semiconductor?
02:01 - What do the letters N and P mean?
02:48 - Bipolar Junction Transistor
04:00 - Transistor as an amplifier
04:10 - Transistor as a switch
04:53 - Transistor Radio
05:24 - Proximity switch
05:48 - PLC output modules
=============================
In this video, we’re going to introduce you to an electronic component called the Transistor.
A transistor is an electronic component found in a variety of circuits and is used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.
There are many different transistor types each with its own electronic symbol.
– BJT or Bipolar Junction Transistor
– FET or Field Effect Transistor
– UJT or Unijunction Transistor
The first stage of making a transistor is the process of changing the semiconductor conducting properties by introducing impurities into its structure. This conduction change process is referred to as Doping.
Simply stated, a P slice of the sandwich is more positive and an N slice of the sandwich is more negative because of Doping.
A transistor is basically a sandwich made of 3 chunks of a semiconductor material doped to make the P chunks more positive, and the N chunks more negative.
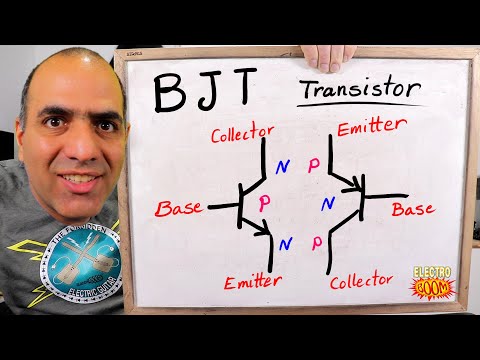
There are 2 types of BJT’s.
They are given names based on the doping content of the semiconductor chunks in each.
One is called an NPN and the other is called a PNP.
Each has its own electronic symbol.
There is a terminal connected to each chunk of the sandwich and each terminal is given a name. The names are Emitter, Base, and Collector.
If we look at controlling a large voltage with a small voltage, we can say that we are performing an amplification. A transistor can do that.
The transistor’s ability to act as a switch or perform a transfer of resistance makes it a very useful component in industrial applications.
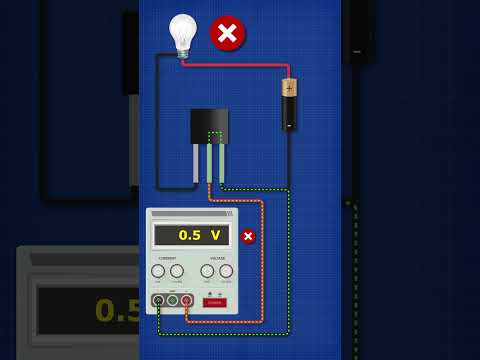
Let’s look at how a transistor works as a switch.
The switch part of the transistor is between the Collector and the Emitter.
The switch is operated by changing the voltage between the Base and the Emitter.
If the input voltage is 0 volts, the switch is open, the resistance is infinite, and the output voltage is +10 volts.
If the input voltage is +10V, the switch is closed, the resistance is zero, and the output voltage is 0 volts.
There are countless transistor applications.
One application that had a huge impact was the invention of the Transistor Radio.
Before the advent of transistors, radios were large bulky pieces of furniture filled with vacuum tubes providing the required audio amplification.
Transistors are used in industry as well.
For example, traditional limit switches are being replaced with active proximity sensors.
The output of an active proximity sensor is a transistor switch. With no moving parts and nothing to wear out or breakdown, the active proximity switch is the hands-down winner over a mechanical limit switch.
Incorporating transistors into PLC output modules is another example of where transistors are used in the industry.
PLC output modules are now built with transistor output circuits.
Early PLCs utilized relay switching to operate loads.
Instead of operating a relay, a PLC module can control the output device with a transistor switch. Again….no moving parts….better reliability and a definite advantage in switching speed!
=============================
You might want to review our previous articles
3-wire Inductive Proximity Sensor | How to Read the Datasheet
Limit Switch Explained | Working Principles
How to Wire Discrete DC Sensors to PLC - Part 2
=============================
Missed our most recent videos? Watch them here:
=============================
To stay up to date with our last videos and more lessons, make sure to subscribe to this YouTube channel:
=============================
=============================
#RealPars #Transistor #Electronic
Комментарии
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:18:20
0:18:20
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:13:57
0:13:57
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:09:31
0:09:31
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:10:48
0:10:48
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:30:17
0:30:17
 0:14:28
0:14:28