filmov
tv
Extreme Value Theorem

Показать описание
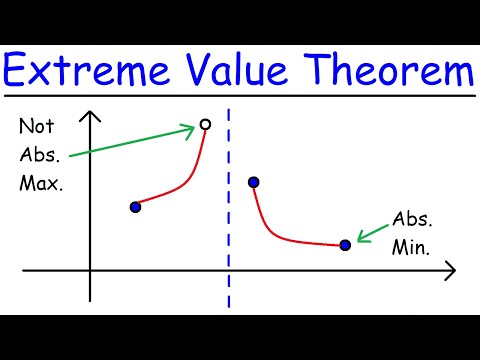
This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the extreme value theorem which states a function will have a minimum and a maximum value on a closed interval. This video provides graphical examples of absolute extrema and relative extrema. It shows you how to identify the absolute maximum and minimum values of a function on a graph. It also explains how to identify the relative maximum and minimum values as well.
____________________________
Introduction to Limits:
Derivatives - Fast Review:
Introduction to Related Rates:
_____________________________
Extreme Value Theorem:
Finding Critical Numbers:
Local Maximum & Minimum:
Absolute Extrema:
Rolle's Theorem:
________________________________
Mean Value Theorem:
Increasing and Decreasing Functions:
First Derivative Test:
Concavity & Inflection Points:
Second Derivative Test:
_________________________________
L'Hopital's Rule:
Curve Sketching With Derivatives:
Newton's Method:
Optimization Problems:
_______________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
____________________________
Introduction to Limits:
Derivatives - Fast Review:
Introduction to Related Rates:
_____________________________
Extreme Value Theorem:
Finding Critical Numbers:
Local Maximum & Minimum:
Absolute Extrema:
Rolle's Theorem:
________________________________
Mean Value Theorem:
Increasing and Decreasing Functions:
First Derivative Test:
Concavity & Inflection Points:
Second Derivative Test:
_________________________________
L'Hopital's Rule:
Curve Sketching With Derivatives:
Newton's Method:
Optimization Problems:
_______________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Комментарии
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:14:50
0:14:50
 0:18:11
0:18:11
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:17:24
0:17:24
 0:32:25
0:32:25
 0:17:17
0:17:17
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:33:45
0:33:45
 0:13:38
0:13:38
 0:09:14
0:09:14
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:15:05
0:15:05
 0:10:17
0:10:17
 0:18:46
0:18:46
 0:11:26
0:11:26
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:31:54
0:31:54
 0:31:10
0:31:10
 1:38:26
1:38:26