filmov
tv
GED Math - Combinations and Permutations

Показать описание
Our mobile app, which has been used by over 50,000 people to help them study, offers thousands of practice GED questions with detailed feedback for every question. Free to install.
•How do you calculate the counting principle?
•For questions in which order matters, what should you do?
More Than One Item
If Jane has three red shirts, two blue shirts, and five green shirts, how many possible outfits could she have?
Use the counting principle to solve problems with more than one type of item. This just means that you multiply the possibilities together.
(3)(2)(5) = 30
Combinations of People in a Line
How many ways can you arrange five people in a line?
Any time you get a problem like this where order matters, it's a factorial. Therefore,
5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120
Toppings on a Pizza
Shawn gets three toppings on his pizza and there are six possible toppings. How many three topping combinations are possible?
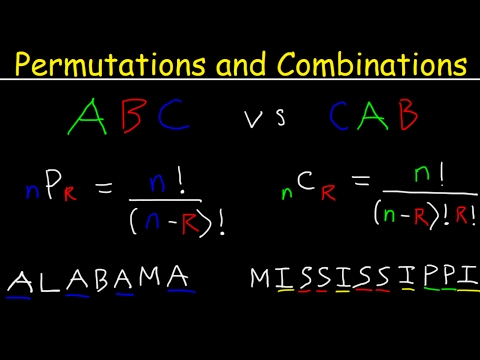
Make a list or a chart with combinations. There are 20 combinations if order does not matter. These 20 combinations are ABC, ABD, ABE, ABF, ACD, ACE, ACF, ADE, ADF, AEF, BCD, BCE, BCF, BDE, BDF, BEF, CDE, CDF, CEF, DEF. Note that the combinations ABC and CBA are the same combination.
Sequences of Award Winners (permutation)
25 students enter the school science fair. Only first, second, and third place are awarded. How many possible sequences of the award winners are there?
This is a permutation, which means we will multiply the numbers into each other. We start with 25 people. Only three people will get awarded by placing in the top three. At the beginning there are 25 possibilities. When first place has been awarded there are 24 possibilities, and when first and second have been awarded, there are 23 possibilities. Multiply these numbers together to find the answer.
25(24)(23) = 13,800
#ged #GedMath
•How do you calculate the counting principle?
•For questions in which order matters, what should you do?
More Than One Item
If Jane has three red shirts, two blue shirts, and five green shirts, how many possible outfits could she have?
Use the counting principle to solve problems with more than one type of item. This just means that you multiply the possibilities together.
(3)(2)(5) = 30
Combinations of People in a Line
How many ways can you arrange five people in a line?
Any time you get a problem like this where order matters, it's a factorial. Therefore,
5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120
Toppings on a Pizza
Shawn gets three toppings on his pizza and there are six possible toppings. How many three topping combinations are possible?
Make a list or a chart with combinations. There are 20 combinations if order does not matter. These 20 combinations are ABC, ABD, ABE, ABF, ACD, ACE, ACF, ADE, ADF, AEF, BCD, BCE, BCF, BDE, BDF, BEF, CDE, CDF, CEF, DEF. Note that the combinations ABC and CBA are the same combination.
Sequences of Award Winners (permutation)
25 students enter the school science fair. Only first, second, and third place are awarded. How many possible sequences of the award winners are there?
This is a permutation, which means we will multiply the numbers into each other. We start with 25 people. Only three people will get awarded by placing in the top three. At the beginning there are 25 possibilities. When first place has been awarded there are 24 possibilities, and when first and second have been awarded, there are 23 possibilities. Multiply these numbers together to find the answer.
25(24)(23) = 13,800
#ged #GedMath
 0:07:08
0:07:08
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:45:47
0:45:47
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:17:41
0:17:41
 0:11:06
0:11:06
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:16:27
0:16:27
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 1:25:01
1:25:01
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 2:51:49
2:51:49
 0:48:36
0:48:36
 0:08:17
0:08:17
 0:27:56
0:27:56
 0:21:52
0:21:52
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:38:51
0:38:51
 0:05:09
0:05:09