filmov
tv
Bond Fundamentals - Definition, Prices And Determining Factors

Показать описание
What is Bond?
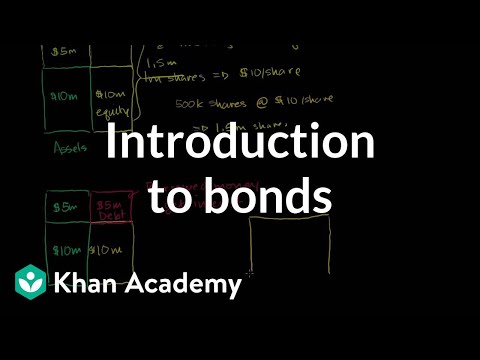
Bond is a special type of debt issued by some entities such as companies, municipalities, states, and sovereign governments. They will use bonds to raise funds to multiple types of projects and operations. It indicates that the investors will lend money to those entities, and bond issuers will offer the fixed income to the bond owners as the return. When those entities are issuing bonds, they will specify the terms of the loan and an interest rate they will be paid to bond owners. They also need to specify the date when the bond principal will be paid back to investors, and that date is called maturity date.
Bond Price and Bond Coupon Rate
The initial price of a bond is called the issue price which indicates the price at which the bond issuer sells the bonds on the date of issue. The par value or the face value of the bond represents the dollar value the issuer will pay back to investors on the maturity day. Similar to bank savings, bond issuers will pay interests to the investors within a regular period based on the predefined interest rate. This rate is also called the coupon rate and the date on which the interest will be paid is called coupon date. For example, a company is issuing a bond with a face value of $1000 with a yearly coupon rate of 5% for 3 years. To attract more investors, they may offer some discounts, say 10% discount on the first day. That means investors just need to pay $900 which is the issue price to get the bond. Every year on the coupon date, the company will pay $50 to bond owners based on the coupon rate. On the maturity date, the company will pay the par value, which is $1000, back to the investors. So, the total profits for this bond with this three-year period would be $50 x 3 + ($1000 - $900) = $250, which roughly equals to an yearly gain of 8%.
The Determining Factors Of Bond Price
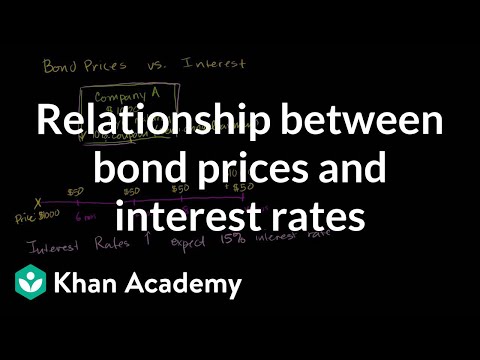
Lots of bonds can be freely traded in the market. The price of the bonds will be determined by a lot of factors. Some important factors include Interest Rates, Inflation, Credit Ratings and Currency Exchange Rates. Generally, the price of bonds will be inversely related with the interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall. When interest rates fall, bond prices rise. For instance, if you are owning a bond with a 2% coupon rate, when the interest is only 1%, your bond will be more attractive compared with bank savings. However, if the bank interest rate rises to 3%, the bond will be less attractive, which will cause more money to flow from the bond market to the banks, and cause the drop of the bond price. The inflation is also an important factor for the bond price. When the inflation is expected to rise in the future, the purchase power of the money will be diluted. So, on the maturity of the bond, the principal you receive by then will buy less things than today. As a result, the rising inflation will cause the bond price to drop and vice versa. Thirdly, the credit ratings of the bonds will also affect their marketing prices. The credit ratings will be issued by some third-party agencies to evaluate the entity's ability to make interest payments and repay the principal on the maturity date. The decreased credit rating indicates that the risk of failure to repay the interests are rising, which will cause the bond price to drop.
Bond is a special type of debt issued by some entities such as companies, municipalities, states, and sovereign governments. They will use bonds to raise funds to multiple types of projects and operations. It indicates that the investors will lend money to those entities, and bond issuers will offer the fixed income to the bond owners as the return. When those entities are issuing bonds, they will specify the terms of the loan and an interest rate they will be paid to bond owners. They also need to specify the date when the bond principal will be paid back to investors, and that date is called maturity date.
Bond Price and Bond Coupon Rate
The initial price of a bond is called the issue price which indicates the price at which the bond issuer sells the bonds on the date of issue. The par value or the face value of the bond represents the dollar value the issuer will pay back to investors on the maturity day. Similar to bank savings, bond issuers will pay interests to the investors within a regular period based on the predefined interest rate. This rate is also called the coupon rate and the date on which the interest will be paid is called coupon date. For example, a company is issuing a bond with a face value of $1000 with a yearly coupon rate of 5% for 3 years. To attract more investors, they may offer some discounts, say 10% discount on the first day. That means investors just need to pay $900 which is the issue price to get the bond. Every year on the coupon date, the company will pay $50 to bond owners based on the coupon rate. On the maturity date, the company will pay the par value, which is $1000, back to the investors. So, the total profits for this bond with this three-year period would be $50 x 3 + ($1000 - $900) = $250, which roughly equals to an yearly gain of 8%.
The Determining Factors Of Bond Price
Lots of bonds can be freely traded in the market. The price of the bonds will be determined by a lot of factors. Some important factors include Interest Rates, Inflation, Credit Ratings and Currency Exchange Rates. Generally, the price of bonds will be inversely related with the interest rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall. When interest rates fall, bond prices rise. For instance, if you are owning a bond with a 2% coupon rate, when the interest is only 1%, your bond will be more attractive compared with bank savings. However, if the bank interest rate rises to 3%, the bond will be less attractive, which will cause more money to flow from the bond market to the banks, and cause the drop of the bond price. The inflation is also an important factor for the bond price. When the inflation is expected to rise in the future, the purchase power of the money will be diluted. So, on the maturity of the bond, the principal you receive by then will buy less things than today. As a result, the rising inflation will cause the bond price to drop and vice versa. Thirdly, the credit ratings of the bonds will also affect their marketing prices. The credit ratings will be issued by some third-party agencies to evaluate the entity's ability to make interest payments and repay the principal on the maturity date. The decreased credit rating indicates that the risk of failure to repay the interests are rising, which will cause the bond price to drop.
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:42:46
0:42:46
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:13:16
0:13:16
 0:07:26
0:07:26
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:09:40
0:09:40