filmov
tv
Ribosomes Structure and Function

Показать описание
#drnajeeb #biology #ribosomes
Ribosomes Structure and Function
This Short is a clip from the lecture "Prokaryotic Protein Synthesis (Translation) - Initiation & Clinical Co-Relates
Type"
To watch this complete lecture please visit our website. 👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻
If you Sign Up Now you can get lifetime access to our premium lectures for just $45 ONLY.
So hurry up and sign up now.
The link is below. 👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻
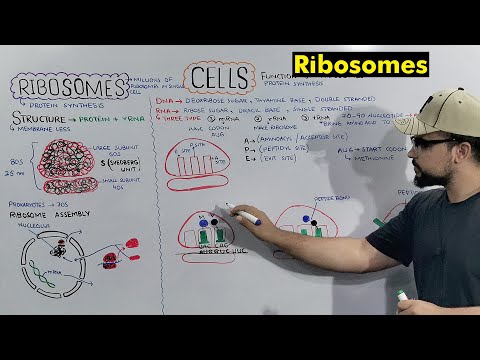
The ribosome functional centers. (a) The two ribosomal subunits. Left: the small ribosomal subunit (T30S). The approximate positions of codon–anticodon interactions of A-, P- and E-tRNAs are shown and the main functional domains are indicated: H, head; L, latch; P, platform; S, shoulder. The arrows designate the approximate directions of the coordinated motions associated with mRNA binding and translocation. The orange arrow on the left of the subunit indicates the creation of the mRNA pore, that is, the latch motion. Right: The large ribosomal subunit (D50S) . Regions that are involved in amino acid polymerization are indicated. These include the two stalks controlling the A-site tRNA entrance (L7/L12) and the E-site tRNA exit (L1), which are known to undergo a coordinated lateral movement during elongation; the positions where the acceptor stems of the three (A-, P- and E-) tRNA molecules interact with this subunit. Insert: a tRNA molecule on which its two functional domains (the anticodon loop and CCA 3 0 end, which binds the incoming amino acid or the newly born protein) are marked. The brown oval indicates the portion of the tRNA molecule interacting with the small subunit, and the blue oval shows the portion bound to the large subunit. (b) The positions of initiation factor 3 (IF3) and Shine-Dalgarno (SD) region on the small subunit. The small ribosomal subunit is shown in gray. The arrow indicates the possible motion of IF3 C-terminal domain (IF3C). Top: a space-filled view similar to that shown in (a). Bottom: a more detailed representation of the opposite view. Marked are the IF3 domains (C terminus, N terminus and the linker between them), the SD region, the anticodon loops of the three tRNAs (A, P and E), and the proteins involved in IF3 binding. (c) The central location of the symmetrical region in the large ribosomal subunit from D50S (gray), with A- and P-site tRNAs and the symmetrical region (blue and green) with its extensions (gold). The symmetrical region is shown in blue and green (for A- and P-sites, respectively) with the pseudo twofold imaginary axis in red. Note that the symmetrical region connects directly or through its extensions (gold) to all the large subunit functional regions, including the bridge, between it and the decoding site on the small subunit.
Ribosomes Structure and Function
This Short is a clip from the lecture "Prokaryotic Protein Synthesis (Translation) - Initiation & Clinical Co-Relates
Type"
To watch this complete lecture please visit our website. 👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻
If you Sign Up Now you can get lifetime access to our premium lectures for just $45 ONLY.
So hurry up and sign up now.
The link is below. 👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻👇🏻
The ribosome functional centers. (a) The two ribosomal subunits. Left: the small ribosomal subunit (T30S). The approximate positions of codon–anticodon interactions of A-, P- and E-tRNAs are shown and the main functional domains are indicated: H, head; L, latch; P, platform; S, shoulder. The arrows designate the approximate directions of the coordinated motions associated with mRNA binding and translocation. The orange arrow on the left of the subunit indicates the creation of the mRNA pore, that is, the latch motion. Right: The large ribosomal subunit (D50S) . Regions that are involved in amino acid polymerization are indicated. These include the two stalks controlling the A-site tRNA entrance (L7/L12) and the E-site tRNA exit (L1), which are known to undergo a coordinated lateral movement during elongation; the positions where the acceptor stems of the three (A-, P- and E-) tRNA molecules interact with this subunit. Insert: a tRNA molecule on which its two functional domains (the anticodon loop and CCA 3 0 end, which binds the incoming amino acid or the newly born protein) are marked. The brown oval indicates the portion of the tRNA molecule interacting with the small subunit, and the blue oval shows the portion bound to the large subunit. (b) The positions of initiation factor 3 (IF3) and Shine-Dalgarno (SD) region on the small subunit. The small ribosomal subunit is shown in gray. The arrow indicates the possible motion of IF3 C-terminal domain (IF3C). Top: a space-filled view similar to that shown in (a). Bottom: a more detailed representation of the opposite view. Marked are the IF3 domains (C terminus, N terminus and the linker between them), the SD region, the anticodon loops of the three tRNAs (A, P and E), and the proteins involved in IF3 binding. (c) The central location of the symmetrical region in the large ribosomal subunit from D50S (gray), with A- and P-site tRNAs and the symmetrical region (blue and green) with its extensions (gold). The symmetrical region is shown in blue and green (for A- and P-sites, respectively) with the pseudo twofold imaginary axis in red. Note that the symmetrical region connects directly or through its extensions (gold) to all the large subunit functional regions, including the bridge, between it and the decoding site on the small subunit.
Комментарии
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:17:33
0:17:33
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:19:38
0:19:38
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:53:16
0:53:16
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:30:03
0:30:03
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:13:23
0:13:23