filmov
tv
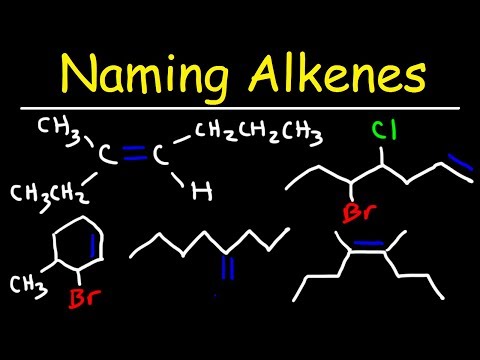
Naming Alkenes

Показать описание
The number of structural isomers increases rapidly as the number of carbons increases because, besides variations in chain length and branching, variations occur in the position of the double bond. IUPAC nomenclature is extremely useful in differentiating among these many alkene compounds.
The IUPAC rules for naming alkenes are similar to those used for the alkanes, with a few additions to indicate the presence and location of double bonds.
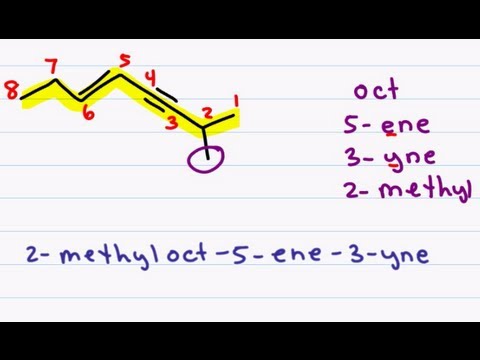
Step 1. Name the longest chain that contains the double bond. The characteristic name
ending is -ene.
Step 2. Number the longest chain of carbon atoms so that the carbon atoms joined by
the double bond have numbers as low as possible.
Step 3. Locate the double bond by the lower-numbered carbon atom bound by the
double bond.
Step 4. Locate and name attached groups.
Step 5. Combine the names for the attached groups and the longest chain into the name.
The IUPAC rules for naming alkenes are similar to those used for the alkanes, with a few additions to indicate the presence and location of double bonds.
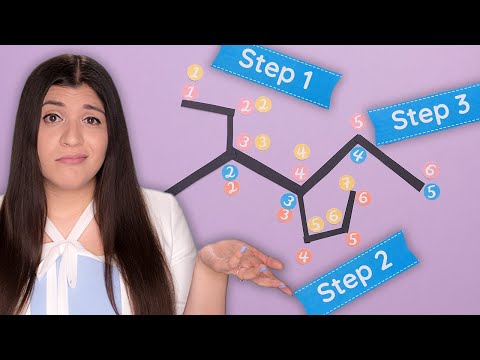
Step 1. Name the longest chain that contains the double bond. The characteristic name
ending is -ene.
Step 2. Number the longest chain of carbon atoms so that the carbon atoms joined by
the double bond have numbers as low as possible.
Step 3. Locate the double bond by the lower-numbered carbon atom bound by the
double bond.
Step 4. Locate and name attached groups.
Step 5. Combine the names for the attached groups and the longest chain into the name.
Комментарии