filmov
tv
How aluminium is extracted by electrolysis
Показать описание
Properties and uses of aluminium.
Properties:
Conducts heat and electricity well. It has a low density for a metal. It does not corrode.
Uses:
Aeroplanes, window frames, foil, drinks cans, electricity cables and pans.
Where does aluminium come from?
Aluminium is extracted from its ore bauxite.
Bauxite is mainly aluminium oxide.
Formula Al2O3
Why is electrolysis used?
Where is aluminium in the reactivity series?
Near the top. It is quite a reactive metal.
Why is electrolysis used?
Why can’t it be extracted using carbon?
It is more reactive than carbon and so carbon cannot remove the oxygen (reduction).
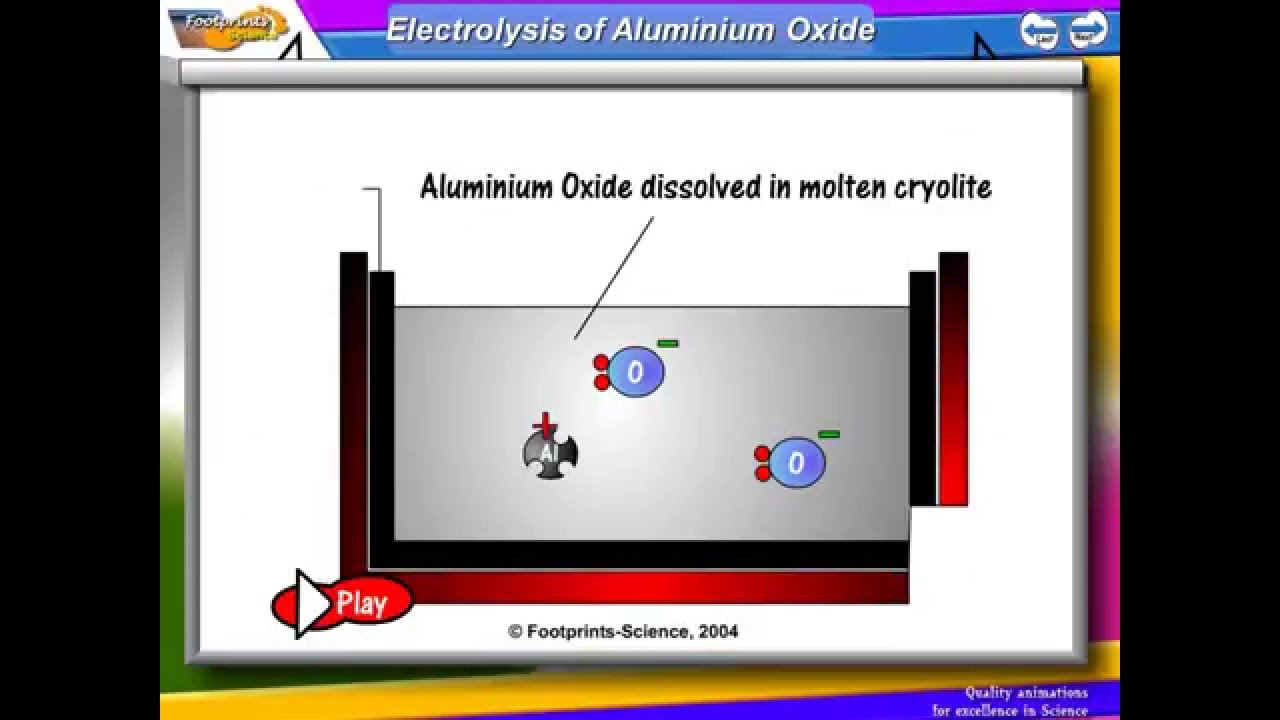
Key features of the electrolysis of aluminium oxide.
Aluminium oxide is molten.
Oxygen is formed at the graphite anode.
The anodes are gradually worn away by oxidation.
Aluminium is formed at the graphite cathode.
The process has a high electrical energy requirement.
Electrolysis of aluminium oxide
Electrolysis of Aluminium Oxide
Electrode reactions.
At the cathode:
Al3+ + 3e- Al
Aluminium ions are reduced (gain electrons) to aluminium atoms .
At the anode:
2O2- - 4e- O2
Oxygen ions are oxidised (lose electrons) to oxygen molecules.
Understanding the process.
Why must the aluminium oxide be molten?
Why are the anodes gradually worn away?
Why is cryolite used?
Why is aluminium expensive?
Answers
The aluminium oxide must be molten for electrolysis to take place. When molten the ions are free to move, in the solid form they are fixed.
The oxygen formed at the anode reacts with the carbon anode to from carbon dioxide.
Answers
Cryolite lowers the melting point and so saves energy.
The electrolytic process requires a lot of electrical energy. Most aluminium extraction plants are located near power stations, usually hydroelectric plants.
Properties:
Conducts heat and electricity well. It has a low density for a metal. It does not corrode.
Uses:
Aeroplanes, window frames, foil, drinks cans, electricity cables and pans.
Where does aluminium come from?
Aluminium is extracted from its ore bauxite.
Bauxite is mainly aluminium oxide.
Formula Al2O3
Why is electrolysis used?
Where is aluminium in the reactivity series?
Near the top. It is quite a reactive metal.
Why is electrolysis used?
Why can’t it be extracted using carbon?
It is more reactive than carbon and so carbon cannot remove the oxygen (reduction).
Key features of the electrolysis of aluminium oxide.
Aluminium oxide is molten.
Oxygen is formed at the graphite anode.
The anodes are gradually worn away by oxidation.
Aluminium is formed at the graphite cathode.
The process has a high electrical energy requirement.
Electrolysis of aluminium oxide
Electrolysis of Aluminium Oxide
Electrode reactions.
At the cathode:
Al3+ + 3e- Al
Aluminium ions are reduced (gain electrons) to aluminium atoms .
At the anode:
2O2- - 4e- O2
Oxygen ions are oxidised (lose electrons) to oxygen molecules.
Understanding the process.
Why must the aluminium oxide be molten?
Why are the anodes gradually worn away?
Why is cryolite used?
Why is aluminium expensive?
Answers
The aluminium oxide must be molten for electrolysis to take place. When molten the ions are free to move, in the solid form they are fixed.
The oxygen formed at the anode reacts with the carbon anode to from carbon dioxide.
Answers
Cryolite lowers the melting point and so saves energy.
The electrolytic process requires a lot of electrical energy. Most aluminium extraction plants are located near power stations, usually hydroelectric plants.
Комментарии
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:12:09
0:12:09
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:30:39
0:30:39
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:03:37
0:03:37
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:29:25
0:29:25
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:17:05
0:17:05
 0:07:29
0:07:29