filmov
tv
Classroom Aid - Special Relativity Introduction

Показать описание
Wiki page
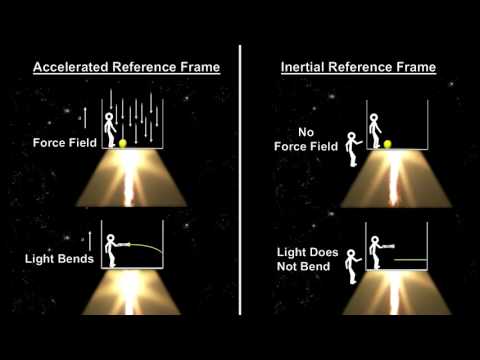
In this segment of the “How Fast Is It” video book we cover the Special Theory of Relativity. We start with the Lorentz Transformations developed after the Michelson-Morley experiment showed that the speed of light was the same for all inertial observers. We then use light clocks to illustrate some of the most striking implications of these new transformations - starting with time dilation and space contraction. As we work through the special relativity effects, we review the physical evidence such as GPS satellites for time dilation and cosmic ray muons for space contraction. We then cover how we add velocities in such a way as to always come up with a number less than or equal to the speed of light. We then use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to illustrate mass-energy momentum increasing without bound as speeds approach the speed of light. The last special relativity effect that we cover is the moving of simultaneity to the realm of the relative.
With this done, we cover Albert Einstein’s motivation for his two Special Theory of Relativity postulates. One was driven by Maxwell’s equations and the other was driven by the inability to detect the Aether. We then cover the geometry of space-time called Minkowski Space. We close with a description of the famous Twin Paradox. For that we use a 50-year trip to Vega and back.
In this segment of the “How Fast Is It” video book we cover the Special Theory of Relativity. We start with the Lorentz Transformations developed after the Michelson-Morley experiment showed that the speed of light was the same for all inertial observers. We then use light clocks to illustrate some of the most striking implications of these new transformations - starting with time dilation and space contraction. As we work through the special relativity effects, we review the physical evidence such as GPS satellites for time dilation and cosmic ray muons for space contraction. We then cover how we add velocities in such a way as to always come up with a number less than or equal to the speed of light. We then use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to illustrate mass-energy momentum increasing without bound as speeds approach the speed of light. The last special relativity effect that we cover is the moving of simultaneity to the realm of the relative.
With this done, we cover Albert Einstein’s motivation for his two Special Theory of Relativity postulates. One was driven by Maxwell’s equations and the other was driven by the inability to detect the Aether. We then cover the geometry of space-time called Minkowski Space. We close with a description of the famous Twin Paradox. For that we use a 50-year trip to Vega and back.
Комментарии
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:21:04
0:21:04
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:36:39
0:36:39
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:02:21
0:02:21