filmov
tv
Fate of pyruvate

Показать описание
Lecture on Fate of pyruvate.
Download the study materials here-
The overall process of glycolysis is:
glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O
If glycolysis were to continue indefinitely, all of the NAD+ would be used up, and glycolysis would stop. To allow glycolysis to continue, organisms must be able to oxidize NADH back to NAD+.
Fermentation
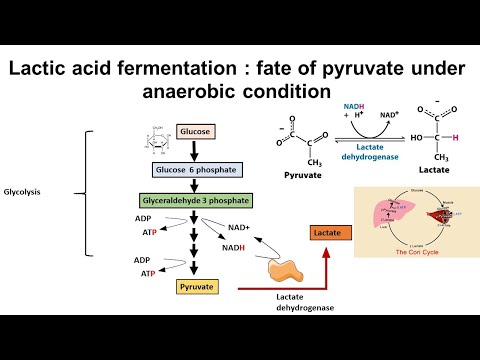
One method of doing this is to simply have the pyruvate do the oxidation; in this process, the pyruvate is converted to lactate (the conjugate base of lactic acid) in a process called lactic acid fermentation:
pyruvate + NADH + H+ → lactate + NAD+
This process occurs in the bacteria involved in making yogurt (the lactic acid causes the milk to curdle). This process also occurs in animals under hypoxic (or partially anaerobic) conditions, found, for example, in overworked muscles that are starved of oxygen, or in infarcted heart muscle cells. In many tissues, this is a cellular last resort for energy; most animal tissue cannot tolerate anaerobic conditions for an extended period of time.
Some organisms, such as yeast, convert NADH back to NAD+ in a process called ethanol fermentation. In this process, the pyruvate is converted first to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide, then to ethanol.
Lactic acid fermentation and ethanol fermentation can occur in the absence of oxygen. This anaerobic fermentation allows many single-cell organisms to use glycolysis as their only energy source. Source of the article published in description is Wikipedia. I am sharing their material. © by original content developers of Wikipedia.
Download the study materials here-
The overall process of glycolysis is:
glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O
If glycolysis were to continue indefinitely, all of the NAD+ would be used up, and glycolysis would stop. To allow glycolysis to continue, organisms must be able to oxidize NADH back to NAD+.
Fermentation
One method of doing this is to simply have the pyruvate do the oxidation; in this process, the pyruvate is converted to lactate (the conjugate base of lactic acid) in a process called lactic acid fermentation:
pyruvate + NADH + H+ → lactate + NAD+
This process occurs in the bacteria involved in making yogurt (the lactic acid causes the milk to curdle). This process also occurs in animals under hypoxic (or partially anaerobic) conditions, found, for example, in overworked muscles that are starved of oxygen, or in infarcted heart muscle cells. In many tissues, this is a cellular last resort for energy; most animal tissue cannot tolerate anaerobic conditions for an extended period of time.
Some organisms, such as yeast, convert NADH back to NAD+ in a process called ethanol fermentation. In this process, the pyruvate is converted first to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide, then to ethanol.
Lactic acid fermentation and ethanol fermentation can occur in the absence of oxygen. This anaerobic fermentation allows many single-cell organisms to use glycolysis as their only energy source. Source of the article published in description is Wikipedia. I am sharing their material. © by original content developers of Wikipedia.
Комментарии
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:15:10
0:15:10
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:08:11
0:08:11
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:10:57
0:10:57
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:15:01
0:15:01
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:29:17
0:29:17
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:05:51
0:05:51