filmov
tv
Every continuous function is measurable||inverse image is measurable LEC 10(measure Theory)

Показать описание
In this Lecture, Students will be able to understand the concept of measurable functions and the following theorems.
1. Let f be any real-valued function defined on a measurable domain D and G an Open set in R. Then f is measurable if and only if f^(-1) (G) is measurable.
2. Every continuous function is measurable.
3. the map of mathematics
@measuretheory1598 @MEASURE THOU THE TIME DILIGENTLY
@brightsideofmaths @mathforall6404 @STANDARDSTUDY @Fematika
#measuretheory #mathematics #measure #maths #continuous #inversefunctions #gate #discrete
1. Let f be any real-valued function defined on a measurable domain D and G an Open set in R. Then f is measurable if and only if f^(-1) (G) is measurable.
2. Every continuous function is measurable.
3. the map of mathematics
@measuretheory1598 @MEASURE THOU THE TIME DILIGENTLY
@brightsideofmaths @mathforall6404 @STANDARDSTUDY @Fematika
#measuretheory #mathematics #measure #maths #continuous #inversefunctions #gate #discrete
Every continuous function is measurable||inverse image is measurable LEC 10(measure Theory)
A continuous function defined on a measurable set is measurable
The Inverse Image of a Set Under a Function: Definition and Examples
Lecture 9: Lebesgue Measurable Functions
f is measurable iff inverse image of every open(Closed) set is measurable
A function is Continuous on X iff for each subset V open in Y, f inverse V is open in X (Proof)
Derivative of continuous function are Measurable
Measurable Function Exercise
Lecture 11 - Measurable functions and continuous functions
11 Measurable functions
3.6 - Measurable functions
prove that every constant function is measurable m.sc. mathematics solution by khushaboo Jafri
Are all sets of measure 0 measurable||Is a measure a measurable function?
PDE Lecture 11 26 Definition of Measurable function and Pointwise Limits
Examples of Measurable functions
Lecture 10.1 Measurable Functions
118C L17P5 Restriction of Measurable Functions
4.1 - Measurable functions
UPB Math 232 LEC7C Measurable Functions
ST342 031 Measurable functions 3 of 3
MEASURE THEORY: Constant functions are measurable and properties of measurable functions
4.1 Measurable Functions II
Proof of Limit of Measurable Functions is Measurable
Inverse Maps - Part 1 - Stories in Real Analysis
Комментарии
 0:28:31
0:28:31
 0:24:22
0:24:22
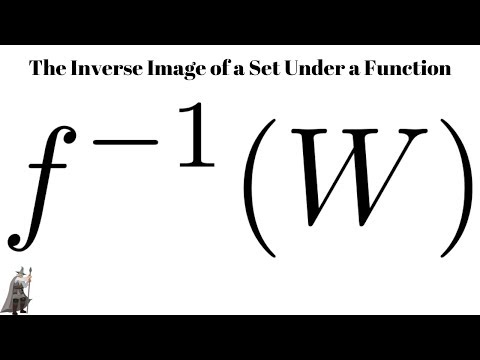 0:06:52
0:06:52
 1:24:57
1:24:57
 0:16:09
0:16:09
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:18:00
0:18:00
 1:12:55
1:12:55
 1:30:53
1:30:53
 0:26:10
0:26:10
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:27:28
0:27:28
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:32:27
0:32:27
 0:29:48
0:29:48
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:21:15
0:21:15
 0:32:27
0:32:27
 0:16:51
0:16:51
 0:06:24
0:06:24