filmov
tv
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (28 of 29) Infinite Cylinder of Charge 3
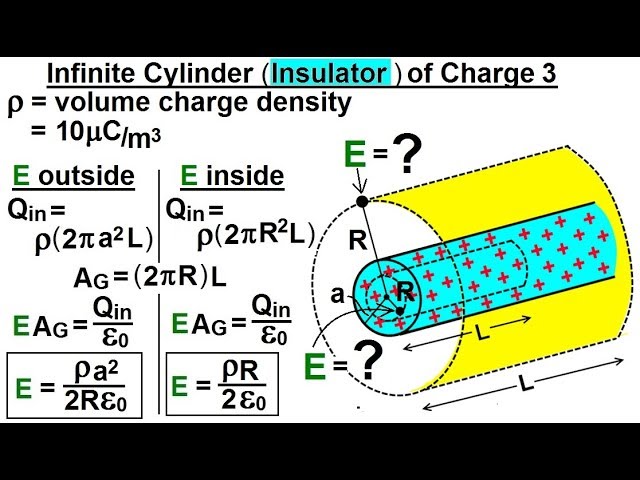
Показать описание
In this video I will find the electric field E=? a distance from an infinite cylinder (cylinder is a INSULATOR, charges evenly distributed inside) of charge where the VOLUME charge density is given.
Next video in this series can be seen at:
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (1 of 29) What is Electric Flux?
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (3 of 29) What is Gauss' Law?
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (9 of 29) Flux=? Through the Gaussian Surface
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (19 of 29) Spherical Insulator: Ex. 1
Physics 37 Gauss's Law (6 of 16) Sphere With Uniform Charge
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (23 of 29) Infinite Slab of Charge 1
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (20 of 29) Spherical Insulator: Ex. 2
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (21 of 29) Line Charge
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (2 of 29) What is Electric Flux?
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (22 of 29) Infinite Sheet of Charge
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (12 of 29) Charges of a Hollow Charge Spherical
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (25 of 29) Infinite Slab of Charge 3
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (24 of 29) Infinite Slab of Charge 2
Physics 37.1 Gauss's Law Understood (18 of 29) Spherical Insulator
Simple question 👀
Physics 37 Gauss's Law (1 of 16) Line Charge
Physics - E&M: Ch 40.1 Current & Resistance Understood (5 of 17) What is Ohm's Law?
Physics 37 Gauss's Law (15 of 16) Variable Charge Distribution: 'Infinite' Slab
Gauss’s Law In One Minute!!
Electric Flux and Gauss’s Law | Electronics Basics #6
Gauss' Law | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M18-01
Ultimate Gauss' Law review
Albert Einstein doing physics | very rare video footage #shorts
Physics 37 Gauss's Law (3 of 16) Spherical Charge
Комментарии
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:06:30
0:06:30
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:06:36
0:06:36
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:14:34
0:14:34
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:28:05
0:28:05
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:09:44
0:09:44