filmov
tv
Theorem: If S is linearly independent then its Subset also Linearly Independent | (Lecture 25)

Показать описание
In this video you will learn Theorem: If S is linearly independent then its Subset also Linearly Independent | (Lecture 25)
Mathematics foundation
Complete Playlist
Vector Spaces
Subspaces
Linearly dependent vectors
Mathematics foundation
Complete Playlist
Vector Spaces
Subspaces
Linearly dependent vectors
L24 | SU{v} is Linearly Dependent iff v in Span(S) | Theorem 1.7 | Linear Algebra | B Sc Hons Maths
Linear Independence
Theorem 4.6.3 (Plus/Minus Theorem)
Theorem: S is Linearly dependent if and only if one vector is linear combination (Lecture 26) Hindi
Plus / Minus Theorem (Section 4.6 Q6)
Linear combinations, span, and basis vectors | Chapter 2, Essence of linear algebra
Orthogonality & Linear Independence (Theorem)
[Linear Algebra] Spanning Set Theorem
Vector Subspace | Linearly Independent | Linearly Dependents Vectors | Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra: The Invertible Matrix Theorem
Subspaces and Span
Superset of linearly Dependent set is linearly Dependent-Theorem -Vector Space-Linear Algebra - 28
Theorem: The Set having elements more than Basis is Linearly Dependent | (Lecture 35) in Hindi
Lecture 15 || Theorem || L(S) of any subset S of a vector space is a subspace of V(F) ||
Linear Algebra 35 | Rank-Nullity Theorem
Replacement Theorem
the many faces of Wilson's theorem
Linear transformations | Matrix transformations | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
Linear Algebra 4.3.2 The Spanning Set Theorem
Linear Extension Theorem
Intruder Theorem
10. Theorem 1 || Orthogonal set of non zero vector is linearly independent
Equivalent Statements Theorem
Existence & Uniqueness Theorem, Ex1
Комментарии
 0:08:13
0:08:13
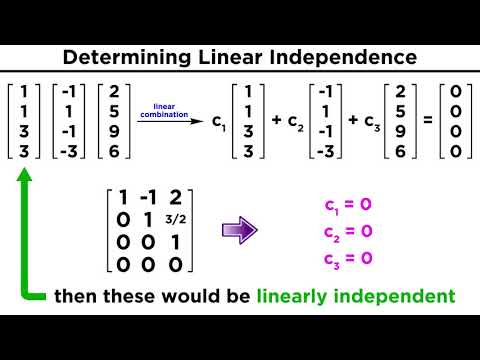 0:12:56
0:12:56
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:09:59
0:09:59
 0:03:19
0:03:19
![[Linear Algebra] Spanning](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lzX4MCTZjU0/hqdefault.jpg) 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:17:10
0:17:10
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:14:34
0:14:34
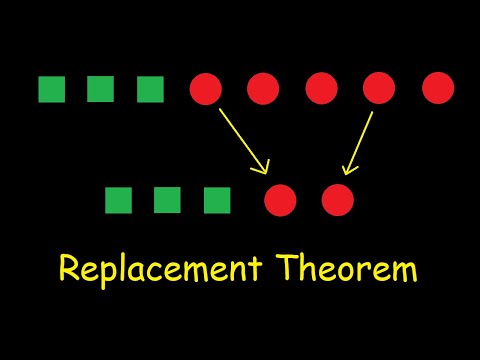 0:32:00
0:32:00
 0:00:46
0:00:46
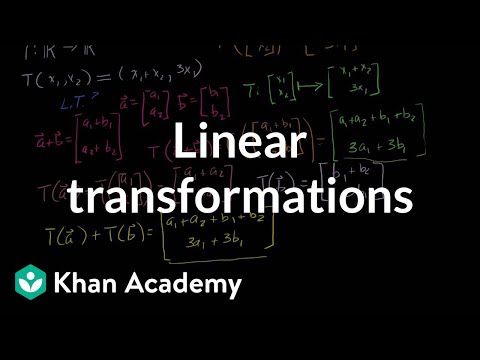 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:18:33
0:18:33
 0:19:32
0:19:32
 0:14:18
0:14:18
 0:11:48
0:11:48
 0:21:03
0:21:03
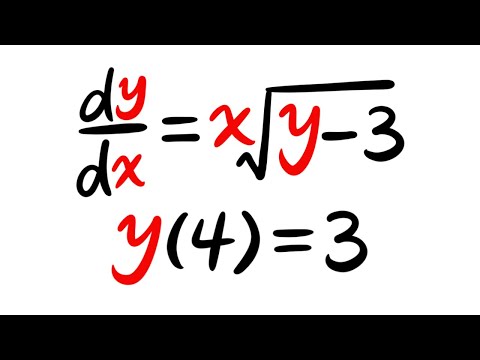 0:11:22
0:11:22