filmov
tv
Vector Decomposition of (2,2,1) Along (1,1,1)

Показать описание
Multivariable Calculus: Decompose the vector u = (2,2,1) as sum of vectors parallel and perpendicular to v = (1,1,1). The key step is to derive the formula for the parallel direction: u_par = proj_v(u) = (u dot v)/||v||^2 v.
For more videos like this one, please visit the Multivariable Calculus playlist at my channel.
For more videos like this one, please visit the Multivariable Calculus playlist at my channel.
Vector Decomposition of (2,2,1) Along (1,1,1)
PHYSICS! vector decomposition, decomposition vectors, how to decompose a vector
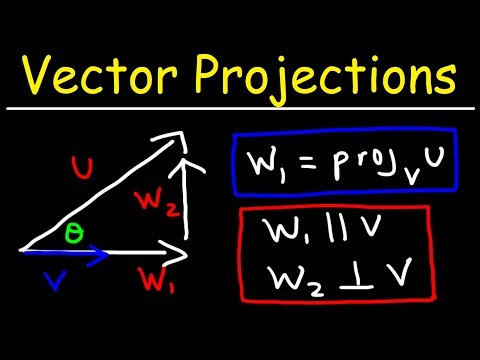
Calculus 3 - Vector Projections & Orthogonal Components
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) Problem | Full Explanation
Linear Algebra 3b2: Decomposition with Geometric Vectors 2
Orthogonal decomposition Example 1.mp4
0.5 Vector Decomposition into components
An example of a singular value decomposition
recursive decomposition in binary multipliers | VLSI design
2. SVD | Singular Value Decomposition | Dimensionality Reduction | Solved Example by Mahesh Huddar
Singular Value Decomposition: 2x2 Concrete Example | Linear Algebra | Ingenium Academy
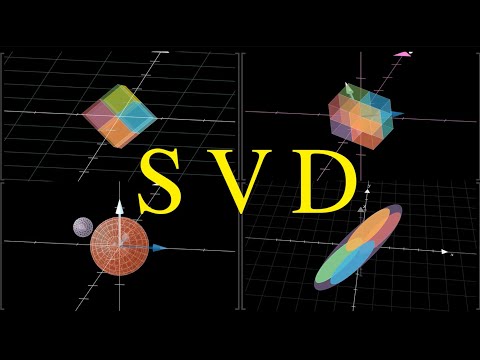
Linear Algebra: Singular Value Decomposition (Full lecture)
Vector Calculus 12: Linear Decomposition by the Dot Product
SVD Visualized, Singular Value Decomposition explained | SEE Matrix , Chapter 3 #SoME2
Linear Algebra 3b1: Decomposition with Geometric Vectors 1
Singular Value Decomposition (the SVD)
Visualize Spectral Decomposition | SEE Matrix, Chapter 2
Orthogonal Decomposition
Vector Decomposition - Part 1 - Foundation
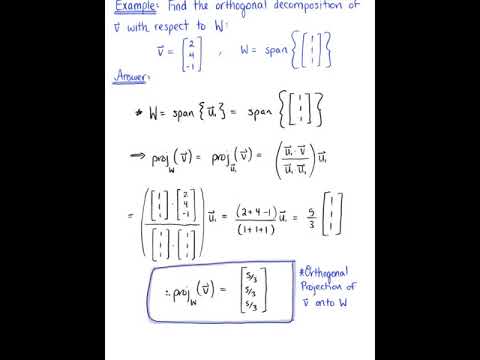
Orthogonal Decomposition (Theorem & Example)
Determine the Singular Value Decomposition of a Matrix
Vector Decomposition - Part 2 - Values of Components
Orthogonal decomposition - example
Singular Value Decomposition
Комментарии
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:12:14
0:12:14
 0:11:27
0:11:27
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:15:49
0:15:49
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:54:01
0:54:01
 0:13:41
0:13:41
 0:16:28
0:16:28
 0:11:28
0:11:28
 0:14:11
0:14:11
 0:15:55
0:15:55
 0:15:02
0:15:02
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:13:14
0:13:14