filmov
tv
Introduction to DNA Replication | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel

Показать описание
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* Oxbridge tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Biology a walk in the park!
The key points covered of this video include:
1. The Importance of DNA Replication
2. DNA Replication in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
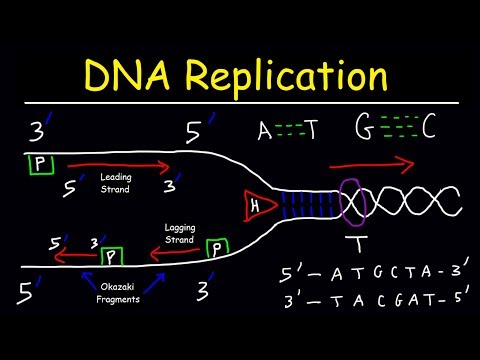
The Importance of DNA Replication
The function of DNA is to contain the genetic information needed for the development and functioning of an organism. Each cell therefore needs to contain a full set of DNA. During the lifetime of an organism, cells must divide for growth, reproduction and to replace old or damaged cells. When a cell divides into two cells, both daughter cells must also contain the full set of DNA. Therefore, all the DNA in a cell must first be replicated. DNA replication takes place during interphase in the cell cycle - this is the phase before the cell starts to divide.
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
In eukaryotes, DNA is stored in long, linear molecules called chromosomes which are found in the nucleus. Before a cell divides, every chromosome in the cell must make an identical copy of itself. Eukaryotes also have circular DNA that is found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. This circular DNA must also be replicated. In prokaryotes, DNA is found as a long, circular loop of DNA with many smaller circular strands called plasmids. All these circular strands of DNA must be copied before the prokaryotic cell is able to divide.
Summary
DNA must be replicated so that DNA can be inherited from parent cells to daughter cells
In eukaryotes, chromosomes in the nucleus and circular DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts must be replicated
In prokaryotes, circular DNA in the nucleoid region and plasmids must be replicated
Комментарии
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 1:07:13
1:07:13
 0:08:19
0:08:19
 0:15:23
0:15:23
 0:19:55
0:19:55
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:14:14
0:14:14
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:51:42
0:51:42
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:18:10
0:18:10
 0:46:23
0:46:23
 0:16:11
0:16:11
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:05:59
0:05:59