filmov
tv
Cardiovascular System | Summary

Показать описание
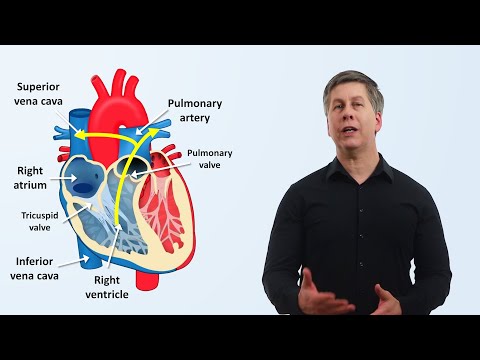
The pulmonary circulation pumps deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart out through the pulmonary trunk to the pulmonary arteries. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs and returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins.
The systemic circulation pumps oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart out through the aorta (the biggest artery in the body) and delivers oxygen to all body organs. Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
The heart contains valves to prevent backflow. The atrioventricular valves separate the atria from the ventricles and prevent backflow when the ventricles contract. The semilunar valves in the aorta and pulmonary trunk prevent backflow into the ventricles during diastole.
The electrical activity of the heart includes a series of autorhythmic pacemaker cells. The sinoatrial node (SA) node, the AV node, the Bundle of His, the bundle branches, and the purkinje fibers pass the electrical signal along, which depolarizes the atria and then the ventricles. In an electrocardiogram, the P wave represents atrial depolarization, the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, and the T wave represents ventricular REpolarization.
Blood - formed elements include erythrocytes (RBCs), leukocytes (WBCs), and thrombocytes (platelets). RBCs carry oxygen to tissues. Each RBC is flexible and light - it doesn't have a nucleus. RBCs are packed with an iron-containing protein called hemoglobin that binds oxygen.
Leukocytes fight infection, and are able to leave the blood vessel to enter infected tissues. Thrombocytes clump together to form part of a blood clot (only when stimulated).
Plasma contains clotting factors that can stimulate the thrombocytes to clump together. Plasma is mostly water, but also contains antibodies, hormones, nutrients, transport proteins, and electrolytes.
Arteries are the biggest and strongest of the vessels, under high pressure and needing a lot of muscle to withstand all that pressure. Arterioles are small but have thick smooth muscle and are the best at constriction and dilation to control blood flow (and in so doing they have the biggest impact on blood pressure of all the blood vessels). Capillaries are microscopic and designed for exchange. Veins return blood to the heart, and are so low in pressure they have to have valves to prevent backflow.
All blood vessels are lined with endothelial cells. These simple squamous epithelial cells are flat, and allow for easy diffusion of nutrients through the cell membrane of capillaries. Unlike the other vessels, capillaries lack smooth muscle, so exchange is perfect here.
Комментарии
 0:23:01
0:23:01
 0:28:32
0:28:32
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:09:26
0:09:26
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:13:36
0:13:36
 0:21:33
0:21:33
 0:23:59
0:23:59
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:13:40
0:13:40
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:16:23
0:16:23
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:48:10
0:48:10
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:05:31
0:05:31