filmov
tv
Complex Numbers-Addition, Multiplication, division, Conjugate, Power, Absolute Value,solve equations

Показать описание
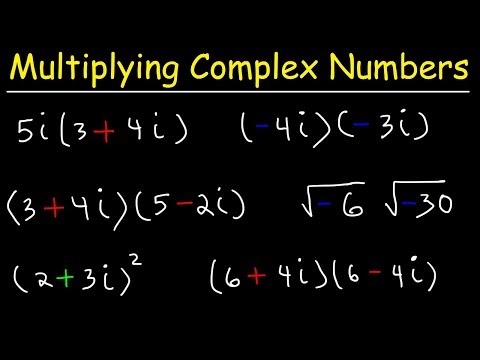
In this video we will learn about complex numbers and their properties, we learn what is the conjugate of a complex number. How to add, subtract, multiply and divide the complex numbers.
we learn about how to raise to a power.
We will learn about absolute value or modulus or magnitude of a complex number.
we will learn about solving equations that their roots are complex numbers and much more.
And how to graphically represent a complex number.
Complex numbers are numbers that extend the concept of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane. They consist of a real part and an imaginary part, and they are used in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields to solve problems that cannot be addressed using only real numbers.
Definition:
A complex number is written in the form:
z=a+bi,
where:
a: The real part of the complex number (Re(z)=a).
b: The imaginary part of the complex number (Im(z)=b).
i: The imaginary unit, defined as i=sqrt(-1)
, with the property that i^2=-1
Complex Plane:
Complex numbers are represented graphically in the complex plane, where:
The horizontal axis (real axis) represents the real part (a).
The vertical axis (imaginary axis) represents the imaginary part (b).
Each complex number corresponds to a unique point in the plane.
Properties and Applications:
Roots of Equations: Complex numbers allow for solutions to equations like x^2+1=0 which have no real solutions.
Algebraic Closure: The set of complex numbers (CC) is algebraically closed, meaning every polynomial equation has solutions in CC.
Applications:
Electrical Engineering: Used to analyze AC circuits using phasors.
Quantum Mechanics: Represent quantum states and wave functions.
Signal Processing: Simplify the representation of sinusoidal signals.
Geometry: Model rotations and transformations.
Fractals and Chaos: Complex numbers are fundamental in generating fractals like the Mandelbrot set.
we learn about how to raise to a power.
We will learn about absolute value or modulus or magnitude of a complex number.
we will learn about solving equations that their roots are complex numbers and much more.
And how to graphically represent a complex number.
Complex numbers are numbers that extend the concept of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane. They consist of a real part and an imaginary part, and they are used in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields to solve problems that cannot be addressed using only real numbers.
Definition:
A complex number is written in the form:
z=a+bi,
where:
a: The real part of the complex number (Re(z)=a).
b: The imaginary part of the complex number (Im(z)=b).
i: The imaginary unit, defined as i=sqrt(-1)
, with the property that i^2=-1
Complex Plane:
Complex numbers are represented graphically in the complex plane, where:
The horizontal axis (real axis) represents the real part (a).
The vertical axis (imaginary axis) represents the imaginary part (b).
Each complex number corresponds to a unique point in the plane.
Properties and Applications:
Roots of Equations: Complex numbers allow for solutions to equations like x^2+1=0 which have no real solutions.
Algebraic Closure: The set of complex numbers (CC) is algebraically closed, meaning every polynomial equation has solutions in CC.
Applications:
Electrical Engineering: Used to analyze AC circuits using phasors.
Quantum Mechanics: Represent quantum states and wave functions.
Signal Processing: Simplify the representation of sinusoidal signals.
Geometry: Model rotations and transformations.
Fractals and Chaos: Complex numbers are fundamental in generating fractals like the Mandelbrot set.
Комментарии
 1:39:35
1:39:35
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:14:58
0:14:58
 0:26:07
0:26:07
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:28:07
0:28:07
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:40:02
0:40:02
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:28:36
0:28:36
 0:33:25
0:33:25
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:12:46
0:12:46
 0:48:36
0:48:36
 0:14:50
0:14:50
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:18:18
0:18:18
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:02:55
0:02:55