filmov
tv
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves

Показать описание
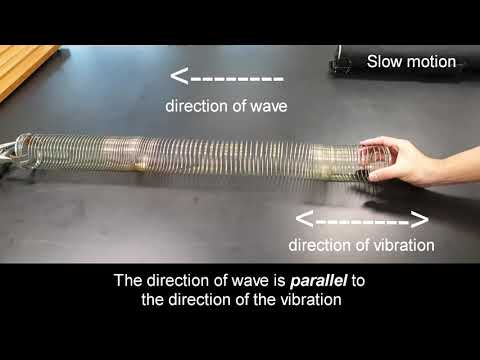
Observe the differences in the movement of transverse and longitudinal waves in a slinky. In transverse waves, the displacement of particles in the wave is perpendicular to the direction of wave travel. In longitudinal waves, the displacement of particles is parallel to to the direction of wave travel.
Throw a pebble into a still pond and it will make a splash. Then ripples appear and move away from the splash in all directions. When the pebble entered the water, its energy from motion was transferred to the water as it pushed the water out of the way. This energy was then spread out in all directions through the ripples – which are small waves in the water. Waves are disturbances that carry energy and travel in a repeating pattern.
Take a length of rope and attach one end to a tree. Holding the other end of the rope, quickly move it up and down. What do you notice?
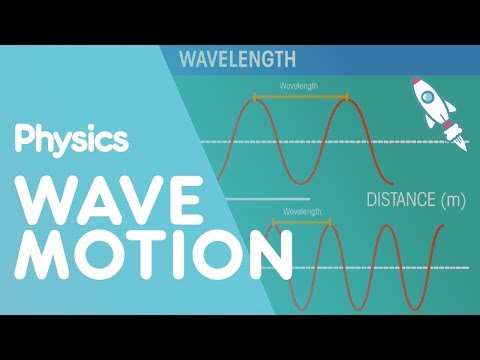
You will see waves move along the rope from your hand to the tree it is attached to. As the waves travel through, the rope moves up and down, perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Waves in which matter moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave are called transverse waves.
Waves moving over the deep ocean surface is an example of transverse waves. Boats floating on the ocean surface move up and down as the waves move perpendicular to the boats. The boats are not moved in the direction of the wave.
Light moves from its source to your eyes in transverse waves too.
Take one end of a slinky spring and give the other end to a friend. Spread apart so that there is some tension in the spring. Gather a small section of spring at your end and hold it together. Let go quickly and you will see a wave move down the slinky to the other end.
As the disturbance moves, the spring gets packed tightly together and then spreads out as the waves passes. The packing together is called a compression and the spreading apart is called a rarefaction. The motion of the spring coils is parallel to the direction of the wave. Such waves are called longitudinal waves. Sounds waves are an example of longitudinal waves. When an object vibrates, the particles of air around the object get compressed and spread out over and over again.
Throw a pebble into a still pond and it will make a splash. Then ripples appear and move away from the splash in all directions. When the pebble entered the water, its energy from motion was transferred to the water as it pushed the water out of the way. This energy was then spread out in all directions through the ripples – which are small waves in the water. Waves are disturbances that carry energy and travel in a repeating pattern.
Take a length of rope and attach one end to a tree. Holding the other end of the rope, quickly move it up and down. What do you notice?
You will see waves move along the rope from your hand to the tree it is attached to. As the waves travel through, the rope moves up and down, perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Waves in which matter moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave are called transverse waves.
Waves moving over the deep ocean surface is an example of transverse waves. Boats floating on the ocean surface move up and down as the waves move perpendicular to the boats. The boats are not moved in the direction of the wave.
Light moves from its source to your eyes in transverse waves too.
Take one end of a slinky spring and give the other end to a friend. Spread apart so that there is some tension in the spring. Gather a small section of spring at your end and hold it together. Let go quickly and you will see a wave move down the slinky to the other end.
As the disturbance moves, the spring gets packed tightly together and then spreads out as the waves passes. The packing together is called a compression and the spreading apart is called a rarefaction. The motion of the spring coils is parallel to the direction of the wave. Such waves are called longitudinal waves. Sounds waves are an example of longitudinal waves. When an object vibrates, the particles of air around the object get compressed and spread out over and over again.
Комментарии
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 1:23:35
1:23:35
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:07:45
0:07:45
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:08:11
0:08:11
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:03:39
0:03:39