filmov
tv
DNA Replication simplified

Показать описание
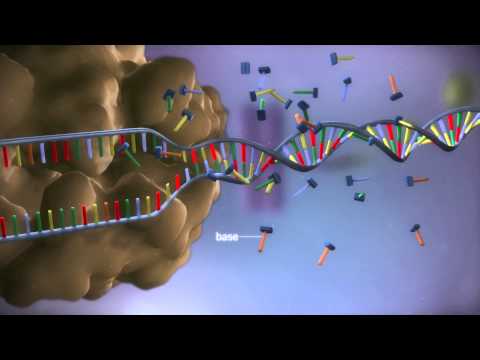
DNA replication is the process by which DNA molecules are copied. It is a fundamental process for all forms of life and is essential for the transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next. The science of DNA replication involves understanding the molecular mechanisms that allow DNA to be accurately duplicated.
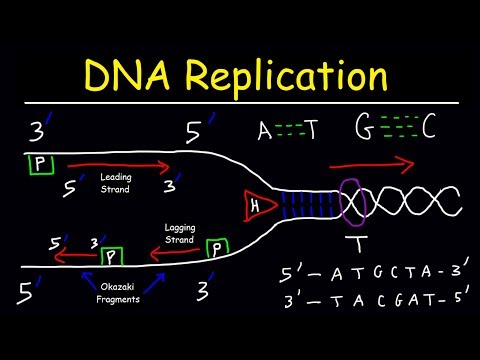
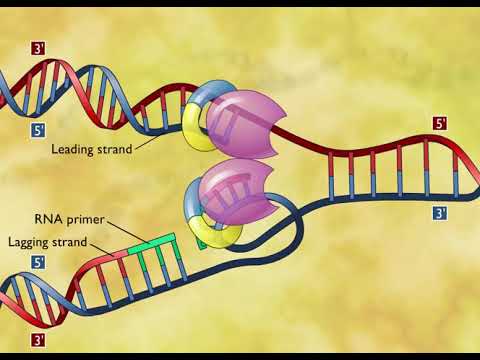
The process of DNA replication begins with the separation of the two strands of the double helix. This is accomplished by the action of an enzyme called helicase, which unwinds the double helix and creates a replication fork. At the replication fork, the two strands of DNA are separated and exposed for replication.
Next, primase, an enzyme, adds RNA primers to the single-stranded DNA templates. These primers serve as a starting point for the DNA polymerase enzymes that will replicate the DNA. The DNA polymerase enzymes add nucleotides to the growing strands of DNA, using the single-stranded DNA template as a guide.
The process of DNA replication is highly accurate, with an error rate of only about one mistake per billion nucleotides. This is achieved through a combination of proofreading and error-correcting mechanisms that ensure that mistakes are caught and corrected before they can be incorporated into the new DNA.
Overall, the science of DNA replication is a complex and fascinating field that has important implications for our understanding of genetics, evolution, and disease.
#sciencefacts #dnareplication #genetics #shorts #biology #biochemistry #everydayscience
The process of DNA replication begins with the separation of the two strands of the double helix. This is accomplished by the action of an enzyme called helicase, which unwinds the double helix and creates a replication fork. At the replication fork, the two strands of DNA are separated and exposed for replication.
Next, primase, an enzyme, adds RNA primers to the single-stranded DNA templates. These primers serve as a starting point for the DNA polymerase enzymes that will replicate the DNA. The DNA polymerase enzymes add nucleotides to the growing strands of DNA, using the single-stranded DNA template as a guide.
The process of DNA replication is highly accurate, with an error rate of only about one mistake per billion nucleotides. This is achieved through a combination of proofreading and error-correcting mechanisms that ensure that mistakes are caught and corrected before they can be incorporated into the new DNA.
Overall, the science of DNA replication is a complex and fascinating field that has important implications for our understanding of genetics, evolution, and disease.
#sciencefacts #dnareplication #genetics #shorts #biology #biochemistry #everydayscience
Комментарии
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:09:16
0:09:16
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:19:55
0:19:55
 1:07:13
1:07:13
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:17:17
0:17:17
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:15:23
0:15:23
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:33:34
0:33:34
 0:14:16
0:14:16
 0:07:57
0:07:57