filmov
tv
peritonitis

Показать описание
Inflammation of peritoneum (a silk-like membrane lining the inner abdominal wall and covering abdominal organs). It is usually due to a bacterial or fungal infection.
Without treatment, death may occur within a few days.
Types:
• Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Develops as a complication of liver disease (e.g. cirrhosis) or of kidney disease.
• Secondary peritonitis: Results from rupture or perforation in abdomen, or as a complication of other medical conditions (e.g. appendicitis, diverticulitis).
• Tuberculosis peritonitis: Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB).
• Chemical peritonitis (sterile peritonitis): Caused by leakage of sterile fluids that are irritants to the peritoneum (e.g. bile, blood, or barium as a contrast agent).
• Peritoneal abscess: Caused by an infected fluid collection.
Symptoms:
• severe pain of abdomen
• swelling of abdomen
• tenderness of abdomen
• weight loss
• fever
Causes:
• perforation of the intestinal tract, stomach ulcer
• pancreatitis, (ruptured) appendicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease
• cirrhosis
Risk factors:
• ascites
• peritoneal dialysis
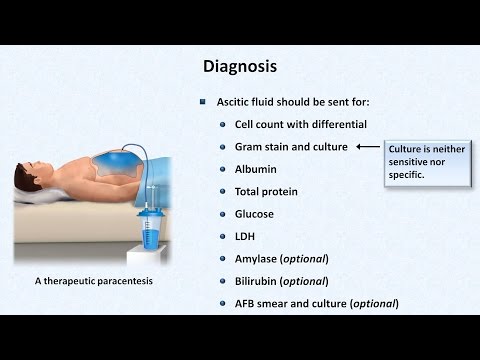
Diagnosis:
• examination
• blood tests
• imaging
Treatment:
• antibiotics: Beta-lactams (penicillins), carbapenems (beta-lactamase-resistant beta-lactams), cephalosporins (semi-synthetic beta-lactams), and quinolones (ciprofloxacin).
• intravenous fluids
• pain medication
• surgery
(The following procedures may be also needed.)
• nasogastric tube
• blood transfusion
Complications:
• shock
• acute respiratory distress syndrome
Without treatment, death may occur within a few days.
Types:
• Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Develops as a complication of liver disease (e.g. cirrhosis) or of kidney disease.
• Secondary peritonitis: Results from rupture or perforation in abdomen, or as a complication of other medical conditions (e.g. appendicitis, diverticulitis).
• Tuberculosis peritonitis: Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB).
• Chemical peritonitis (sterile peritonitis): Caused by leakage of sterile fluids that are irritants to the peritoneum (e.g. bile, blood, or barium as a contrast agent).
• Peritoneal abscess: Caused by an infected fluid collection.
Symptoms:
• severe pain of abdomen
• swelling of abdomen
• tenderness of abdomen
• weight loss
• fever
Causes:
• perforation of the intestinal tract, stomach ulcer
• pancreatitis, (ruptured) appendicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease
• cirrhosis
Risk factors:
• ascites
• peritoneal dialysis
Diagnosis:
• examination
• blood tests
• imaging
Treatment:
• antibiotics: Beta-lactams (penicillins), carbapenems (beta-lactamase-resistant beta-lactams), cephalosporins (semi-synthetic beta-lactams), and quinolones (ciprofloxacin).
• intravenous fluids
• pain medication
• surgery
(The following procedures may be also needed.)
• nasogastric tube
• blood transfusion
Complications:
• shock
• acute respiratory distress syndrome
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:18:32
0:18:32
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:08:31
0:08:31
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:14:19
0:14:19
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:17:11
0:17:11
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:12:47
0:12:47
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:07:07
0:07:07
 0:58:03
0:58:03