filmov
tv
Phlebotomy Essential Techniques

Показать описание
Phlebotomy:
Definition
Phlebotomy: The process of collecting blood samples from patients for laboratory testing and analysis.
Importance
1. Accurate diagnosis and treatment of diseases
2. Monitoring of patient health and response to treatment
3. Research and development of new medical treatments and technologies
Key Steps
1. Patient preparation and identification
2. Selection of appropriate equipment and supplies
3. Vein selection and preparation
4. Venipuncture (blood collection)
5. Post-collection care and processing
Types of Phlebotomy
1. Venipuncture (blood collection from veins)
2. Capillary puncture (blood collection from capillaries, often used for pediatric or geriatric patients)
3. Arterial puncture (blood collection from arteries, often used for blood gas analysis)
Equipment and Supplies
1. Needles and syringes
2. Tourniquets
3. Antiseptic wipes and solutions
4. Blood collection tubes and containers
5. Gloves and personal protective equipment (PPE)
Safety Precautions
1. Proper hand hygiene and use of PPE
2. Safe handling and disposal of sharps and biohazardous materials
3. Prevention of needlestick injuries and exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Challenges and Complications
1. Difficulty finding suitable veins
2. Patient anxiety and discomfort
3. Hematoma or bruising at the collection site
4. Infection or contamination of the collection site
Best Practices
1. Follow established protocols and guidelines
2. Use proper technique and equipment
3. Ensure patient comfort and safety
4. Continuously update knowledge and skills
These notes cover the basics of phlebotomy, including its importance, key steps, types, equipment, safety precautions, challenges, and best practices.
Definition
Phlebotomy: The process of collecting blood samples from patients for laboratory testing and analysis.
Importance
1. Accurate diagnosis and treatment of diseases
2. Monitoring of patient health and response to treatment
3. Research and development of new medical treatments and technologies
Key Steps
1. Patient preparation and identification
2. Selection of appropriate equipment and supplies
3. Vein selection and preparation
4. Venipuncture (blood collection)
5. Post-collection care and processing
Types of Phlebotomy
1. Venipuncture (blood collection from veins)
2. Capillary puncture (blood collection from capillaries, often used for pediatric or geriatric patients)
3. Arterial puncture (blood collection from arteries, often used for blood gas analysis)
Equipment and Supplies
1. Needles and syringes
2. Tourniquets
3. Antiseptic wipes and solutions
4. Blood collection tubes and containers
5. Gloves and personal protective equipment (PPE)
Safety Precautions
1. Proper hand hygiene and use of PPE
2. Safe handling and disposal of sharps and biohazardous materials
3. Prevention of needlestick injuries and exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Challenges and Complications
1. Difficulty finding suitable veins
2. Patient anxiety and discomfort
3. Hematoma or bruising at the collection site
4. Infection or contamination of the collection site
Best Practices
1. Follow established protocols and guidelines
2. Use proper technique and equipment
3. Ensure patient comfort and safety
4. Continuously update knowledge and skills
These notes cover the basics of phlebotomy, including its importance, key steps, types, equipment, safety precautions, challenges, and best practices.
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:06:01
0:06:01
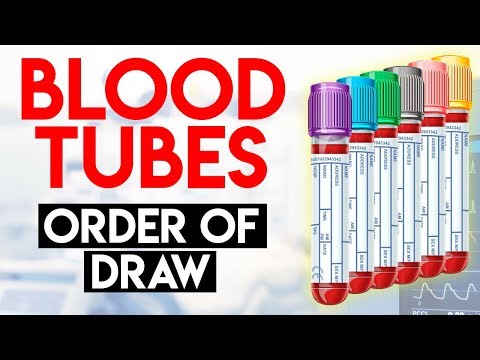 0:22:56
0:22:56
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:05:46
0:05:46
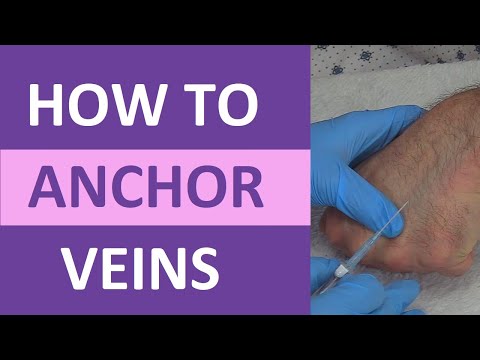 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:05:52
0:05:52
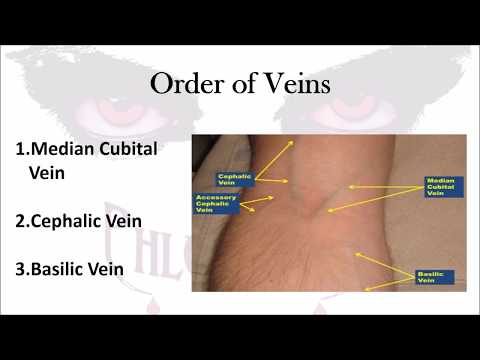 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:11:59
0:11:59
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:29:25
0:29:25
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:47:57
0:47:57
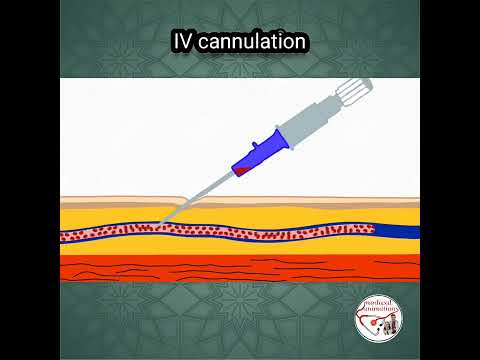 0:00:27
0:00:27