filmov
tv
Prove that the limit of √(n+√n) - √n = 1/2 (ILIEKMATHPHYSICS)
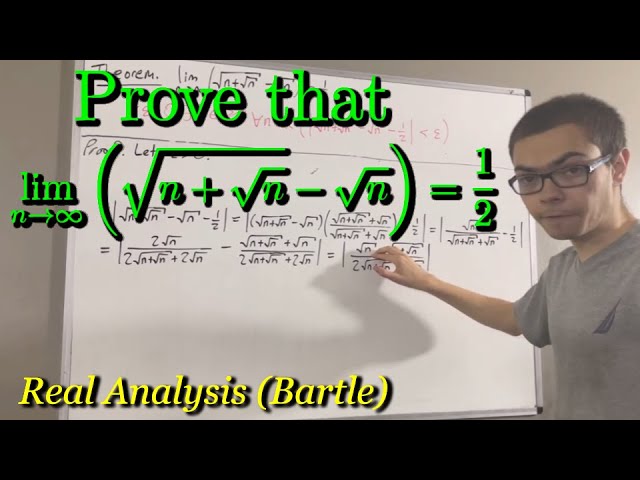
Показать описание
This video references the book "Introduction to Real Analysis" by Bartle and Sherbert (Fourth Edition). For more details regarding the techniques used in this video, see Section 2.4 and Section 3.1.
Thanks and enjoy the video!
Thanks and enjoy the video!
Proof of a Limit Value Using Epsilon and Delta
Definition of the Limit of a Sequence | Real Analysis
proving the limit of a product is the product of the limits, epsilon-delta definition
Proof: The Limit of a Sequence is Unique | Real Analysis
This is a very famous limit
1.7 Proving a Limit: x^2 = 4 (advanced)
The most important limit in Calculus // Geometric Proof & Applications
Limit Laws - Proof of Sum Law
How To Find The Limit At Infinity
Epsilon delta limit (Example 4): Limits at infinity
The Most Important Limit In Calculus
Proof: Central Limit Proof
How to prove that the limit does not exist (KristaKingMath)
The Limit of a Sequence is Unique Proof
The Limit (do not use L'Hospital rule)
How to Prove that the Limit of (2n + 1)/(3n + 7) as n approaches infinity is 2/3
Prove the limit does not exist. Real Analysis Example (2.1)
Proving All the Sequence Limit Laws | Real Analysis
Simple Limit Proof Using Epsilon-Delta Definition of a Limit
2.9 How to prove a limit DNE from the definition
Proof: Limit of sinx/x as x approaches 0 with Squeeze Theorem | Calculus 1
Epsilon Delta Proof of a Limit 1
Limit of a Composite Function Theorem: Proof
2.11 Proof of the limit law for sums
Комментарии
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:28:27
0:28:27
 0:13:22
0:13:22
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:14:04
0:14:04
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:13:14
0:13:14
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:35:14
0:35:14
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:11:39
0:11:39
 0:12:35
0:12:35
 0:54:07
0:54:07
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:08:21
0:08:21